In order for a rebuilt house to serve for many years, being strong and reliable, it needs not only a good foundation. No less significant element is the roof truss system, which takes on all the vicissitudes of the weather. And with honor, she must withstand loads in the form of gusts of wind, heavy snowfalls and heavy rains. Let's talk about how it is arranged and how to build this system correctly.

Requirements for the truss system
Stiffness
First of all, every detail of the system, as well as the joints, must be rigid without being deformed neither with shear nor with thrust. The basis of the whole structure is a triangle. It is this form that frames (trusses) have, which are fixed parallel to each other. Their rigid fixation provides the roof with the necessary stability. But if the farm turned out to be mobile, close to trouble. Such an inferior roof itself may collapse, and the walls collapse.
Low weight
The roof should not be heavy, so the system of rafters, as a rule, is made of wood. If the weight of the roof is solid, then the base is made of metal. Or take a coniferous tree, not lower than the first grade, with moisture below 18 percent. The use of antiseptic treatment and the use of fire retardants for fire protection are two prerequisites. Then the mounting points of the roof truss system will be strong and strong.
High quality material
The tree for the rafters should be as follows:
- The wood is taken 1 - 3 grades. Cracks and knots should be at a minimum. There can be 3 knots per meter with a height not exceeding 3 cm. Cracks are permissible not over the entire depth, up to half the length of the board.
- Bearing elements are made of wooden parts with a thickness of 5 cm and an area of 40 cm 2 .
- Coniferous boards can be up to 6.5 m long, and hardwood - up to 4.5 m.
- Runs, pillows and mauerlat are made from solid hardwood. They are treated with antiseptic.
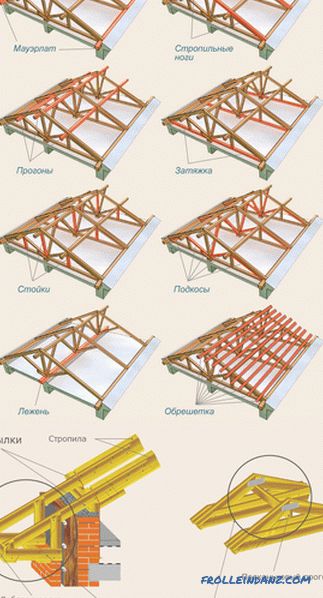
The main parts of the construction of the truss system
Thinking through the device of the truss system of the roof, it is necessary to know what details this system consists of.
# 1. Mauerlat is like the foundation of the whole system. It helps to evenly distribute the load on the walls.
# 2. The rafter foot determines the angle of inclination of the slope, as well as the general appearance of the roof, rigidly fixing individual elements.
# 3. Run - fastens feet of rafters. The ridge run is at the top, the side runs are on the side.
# 4. Tightening - does not allow rafter legs to disperse, connecting them below.
# 5. Racks and struts - give the rafters extra stability. They rest on the floor (which lies below parallel to the ridge).
# 6. Crate - it is perpendicular to the rafter legs and is cut boards or boards. It is designed to transfer the entire load from the roofing material to the rafter legs.
# 7. The ridge of the roof is the junction of two roof slopes. Along the ridge is crammed solid crate to enhance this part of the roof.
# 8. Fillers - used to create an overhang in case the length of the rafter legs is not sufficient.
# 9. The roof overhang is an element intended to protect excessive precipitation from falling on the walls.
Now consider such a complex knot as a roof truss. It has a flat shape, and includes, in addition to the rafters, extensions, racks and braces. They are placed so that the load on the walls inside the house does not occur. Only its external walls are supports, and the load goes vertically. The distance between the trusses is determined by calculations. If the span is large, then the farm consists of several parts. In the attic, the lower farm belt serves as a ceiling.
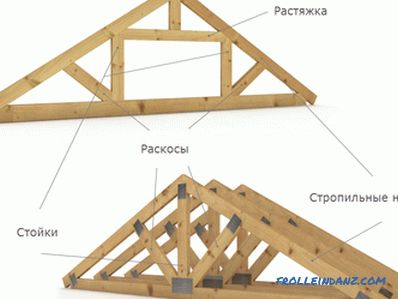
The above are examples of wooden trusses, besides this, in some cases, trusses made of concrete and metal are used.
Forms of roofs and roof systems
Shed roof.
The simplest device of the truss system has a roof with one slope, which is inclined at an angle from 14 to 26 °. If the house is small, and its span does not exceed 5 m, then a rafter-type rafters system is needed. It rests on the outer walls, as well as on the wall inside the building (if there is one). When the span of more than 5 m, you need to use trusses.
Device of a single shed roof.
Gable roof
The roof with two slopes is also simple, with an attic or attic located under it. Its slope is from 14 to 60 °. If the outer walls are less than 6 meters apart, they make a hanging truss system. Suspended rafters should be used when the span is large and there are internal supports.
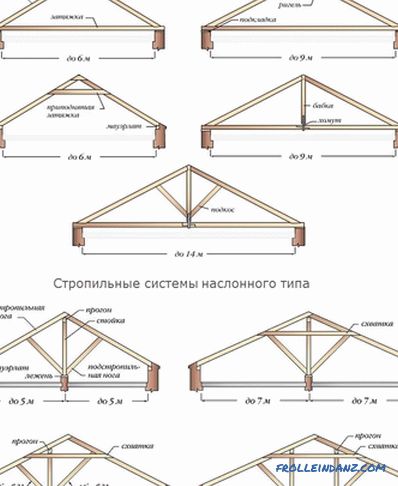
Device for hanging and wall gable roof rafters.
- Details about it in the material: The rafter system of the dual-pitch roof and its device
The four-pitch roof
The roof with four slopes is called a hip or semi-gated. Its slope is from 20 to 60 °, and the span can be up to 12 m. At the same time, there should be internal supports. Gable walls in this case are absent, which saves materials. However, the installation of such a roof is more complicated than the double-slope. For this roof structure, roof systems are made either of the glazing type, or with the use of roof trusses.
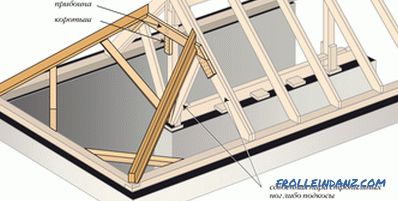
Design features of the hip roof.
Broken roof
The roof is broken, or attic, at the bottom can have a slope of up to 60 °. But at the top it is usually more gentle. Due to this, the area of the attic increases. Such a roof is good for houses where the width does not reach 10 m. As in the previous cases, you can use a railing system on the wall. However, farms are preferable to use.
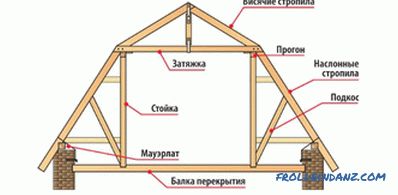
The device is a broken roof.
- Above are listed the most common, but not all forms of roofs, for more details see the material: Types of roofs of private houses by construction and geometric forms
Types of roof systems - how they differ among themselves
One or another type of truss system is chosen not spontaneously, but depending on the construction of the house under construction and its dimensions. Further on each type of roof systems.
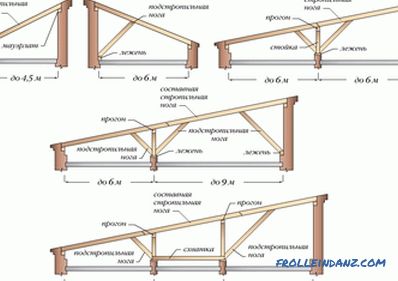
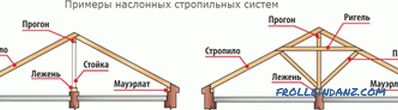
System with hanging rafters
They are good for roofs with two slopes, where the span is no more than 6 meters, and there are no walls inside. At the bottom, the rafter serves as a mauerlat, and at the top - they lean on each other. There is also a tightening that reduces the rafters on the walls of the house. Beam puffs are placed at the very bottom of the rafter legs - they also serve as floor beams. By the way, the overlap of the upper floor, made of reinforced concrete, can also play the role of a puff. If the tightening is done higher, it is already called a bolt. If the span between the outer walls is more than 6 m, it is necessary to use support posts and braces to support the rafter legs. At the same time, the length of the lower part of the rafters, i.e. the parts after the support, must be no more than 4.5 m.
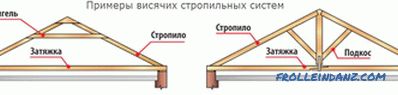
We list several important facts about their design:
- It is not necessary to rest the overhang of the roof on the bottom of the rafters extended beyond the wall. Much better to support such roof truss systems will fit the filly (with the width of the overhang do up to a meter). And then the leg will be the whole plane to lean on the mauerlat. The section of the fillies is usually smaller than the section of the truss legs.
- On the slope, you must nail the wind board, from the ridge to the power plate. The slope is made from the attic. This is necessary so that the roof becomes rigid, does not wobble and is not destroyed by the wind.
- If the humidity of the wooden roof material is more than 18%, get ready for the fact that the system of rafters can become shaky after the wood has dried. Therefore, connect such a tree not with nails, but with bolts - they can be tightened in case of anything. Better yet, use screws or wicked nails.
Suspended roof systems
They are suitable for roofs where the span is from 10 to 16 m. Any slope can be, and inside the building there should be supporting walls or columns. Above the rafters are based on the ridge girder below - Mauerlat. The ridge is supported either by the inner wall (we lie down) or by the uprights. Since the loads are only vertical, there is no need for tightening.
When the span is large (up to 16 m), you can replace the skate girder with two side ones, which will rest on the stands. To rafter legs do not bend, need struts and crossbars. If you make an attic, you can make a wall with the support of the nylon walls, the height of which is from 1 to 1.5 m. Well, or use a broken roof attic (with sloping slopes).
What you need to pay special attention to:
- Each of the elements of this system should not be less than 5 cm thick.
- A smooth glued surface of all nodes of the truss system is a necessary condition. So they will not rot and will not be so much exposed to the fungus.
- Adding additional units "from the lamp" into the calculated rafter system is prohibited. Otherwise, the load may occur at all where it is needed.
- Mauerlat (his sole) is obliged to lie strictly horizontally relative to the walls. Requires horizontal position and the surface of the docking of the power plate with a rafter foot. Otherwise, the support may tip over.
- Racks and struts are arranged as symmetrically as possible.
- So that the rafters do not get wet and do not rot, they do good ventilation. To do this, in the roof of the attic provide a gap in the roof of the attic - airs.
- Where rafter knots are joined with masonry, waterproofing is needed. And then the condensate will ruin the tree.
- Without a support or strut, the foot of the rafter is no longer than 4.5 m.
Connectors
In order for the roof to be reliable, the truss system components must be correctly connected. It is necessary to take into account the direction and strength of the loads (both static and dynamic). And it is also important to foresee the possible cracking of the wood from shrinkage, making it so that the rafter system components do not cease to function properly.
Previously, all parts of the truss system were fastened together by cuttings. It is reliable, but not too economical. After all, for this it is necessary that the wooden structures have large sections that would allow making the cuts safely loosening the wooden elements.
Therefore, at the present time, the rafters are fastened not with cuts, but with bolts and bolts.
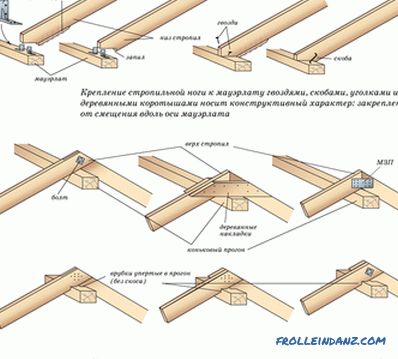
Ways of attaching rafter legs.
The use of perforated steel plates with a corrosion-resistant coating is popular. Fix the lining nails or plates with teeth, recessed into the tree. Such fasteners for the roof system is convenient in that:
- Pads reduce wood consumption by one-fifth, since smaller sections are required than with a cut;
- they can be mounted by a master with no very extensive experience;
- they are fixed very quickly.
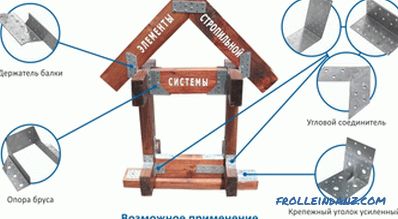
Perforated plates used for attaching rafters.
Lastly, you can watch a useful video which tells about all the most important points in the design of the roof truss system.
The material was prepared by the authors of the SRBU project. RU
Video: Roof railing system you need to know to properly design