Wooden structures are increasingly used in modern construction. Houses, farm buildings of various purposes, arbors, built of wood, look harmonious, beautiful and safe from the point of view of ecology.

Due to the fact that a tree has such property as decay, it must be treated with special means before construction.
As a result of this widespread use of wood, demands on the reliability and durability of buildings increase. And the protection of wooden structures from decay, in the circumstances, is fundamental. After all, protected wood, regardless of the chosen method, will last a long time and will not need to be repaired or replaced.
Types of wood protection from rotting

Scheme of wood lesion with fungus.
The decay process itself is the destruction of a tree by the fungi that feed on it. Moreover, fungal spores can come from various sources: a forest, a warehouse where the storage of wood was organized incorrectly. However, the most dangerous are house fungi, which are formed during operation. They cover the top layer of wood with white cords and films that resemble cotton wool in their structure.
As a result, the wood in a short time becomes brown, loose, cracked and finally collapses. The process of rotting wood is possible at a temperature of 5-45 ° C, humidity of 20% -80%, in the presence of air. In the cold season, even while in the water, the wood does not rot, and dry - all the more. Therefore, protection from decay of wood is reduced to ensure that at least 1 condition for the occurrence of dangerous fungal formations.
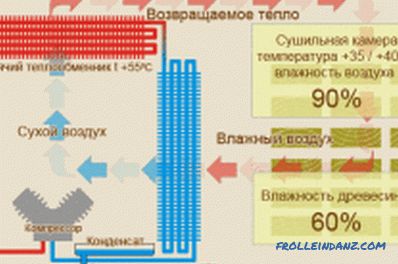
Scheme of wood drying in special dryers.
The best way to protect against putrefactive processes is to rid the wood of moisture. The easiest way is to use other building materials for the construction of premises with high humidity. In addition, wooden structures should be built from wood that has been dried in special dryers at high temperature (up to 130 ° C). When using just such a building material, it is possible to completely exclude the entry of putrefactive fungi from the forest.
Types of protection:
- constructive;
- preventative;
- physical;
- protective coating method.
In addition, protection against the ingress of moisture can be performed with or without an antiseptic coating. Chemical, complex protection, and also sterilization of wood are possible.
Structural protection: nuances

In order to protect the tree from moisture, it is necessary to install a roof with a slope.
When using not until the end of dried wood in construction, for its final drying already in the finished structure and in order to avoid the ingress of moisture, constructive protection is further applied. To prevent rain and water from snow from sinking wood, roofing is carried out with slopes, and drains along the roof must not only be provided, but also periodically cleaned of accumulated debris (foliage, small branches).
In addition, a waterproofing layer must be laid on top of the batten, which is necessary for fixing the roofing material. As it can be a special film or roofing material. Moreover, the first layer of waterproofing is placed perpendicular to the batten boards, and the second layer - perpendicular to the 1st. This method of installation allows you to maximize protection and limit the penetration of moisture, even if the roofing material is damaged. The strips of waterproofing material are attached either by building brackets and a stapler, or by nails with a wide cap. In this case, the joints are further glued together with tape.
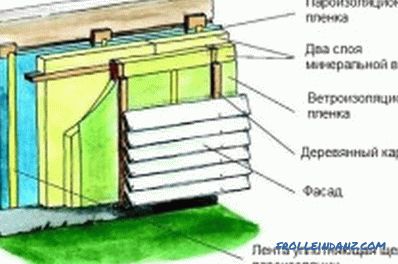
The vapor barrier for the walls of a wooden house.
When arranging the lower ties of buildings of any purpose, a layer of waterproofing material is laid on the foundation. This will avoid moistening the strapping with moisture from the soil. In addition, when performing exterior finishing works, the moisture-resistant material covers not only the walls of the facade, but also captures the bottom trim and part of the foundation.
A layer of vapor insulating material that is attached to the inside of the roof will protect the sheathing boards from moisture, which can be formed as a result of a difference in the internal air temperature and the outside during the cold season. Fastening is performed using a construction stapler and staples or nails with a wide cap.
Chemical protection: recommendations
But constructive protection is not the only one that is used to protect wood from excess moisture. When attaching waterproofing materials, vapor barrier, installation of the roof may cause mechanical damage to wooden structures.And to protect gazebos, bridges and other wooden structures that are constantly on the street, only constructive methods are not possible. After all, they are exposed all year round to the environment: rain, precipitation and melting of snow, groundwater. In this case, the use of chemical protection is inevitable.
Chemical protection is the impregnation of wood with special compounds that are toxic for fungal formations.
Such solutions are water-soluble and oil-based.
Water-based antiseptics contain solutions of sodium fluoride or sodium fluoride with the addition of a dye. It is the presence of the dye that allows you to visually determine the raw areas of wood. Water-soluble antiseptic compositions are odorless and do not cause harm to human health. Most often, this treatment is used for materials made of wood, which will later be used in rooms where this solution cannot be washed off with water.
An oil-based antiseptic contains creosote, shale oil. These are toxic substances for fungi, however, when applying them, you must take maximum precautions. This chemical composition is harmful to human health and smells unpleasant. But such protective antiseptics are not washed out with water and can be used for wooden structures that are in the open air. Their lifespan is extended for several years without additional processing.
Didn't find the answer in the article? More information on the topic:
-

How should I properly caulk a bath?
Instructions on how to properly caulk a bath. A list of tools for the job, recommendations for choosing a compactor for a log house, as well as a description of two caulking methods.




