There are two main goals at the roof of the house: protecting the house from adverse weather conditions and maintaining heat inside the house. The basis of the carrying capacity of the roof, which can withstand the weight of the roofing material, and strong wind blows, and the weight of snow in the winter or rain flows in the summer, is the system of rafters.
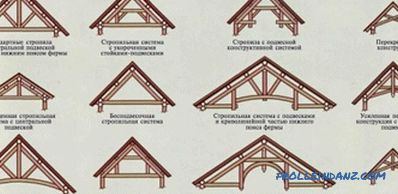
Versions of truss structures.
The length of the rafter directly depends on the distance from the ridge of the roof to the top of the wall. Quite often, when constructing a truss system, it turns out that the standard length of a bar or board available is not enough to construct a truss system. In this case, building or splicing rafters is used.
Building or splicing - what's the difference?
The main elements of the roof truss system are vertical pillars, struts and obliquely laid truss legs. Rafter legs are placed on the upper ends on a special beam girder mounted on vertical racks, and on the lower ones - on a special support beam laid on the wall — the power plate. The cross section of the truss system is directly dependent on the expected load on the roof, and their length - on the geometric dimensions of the slope.
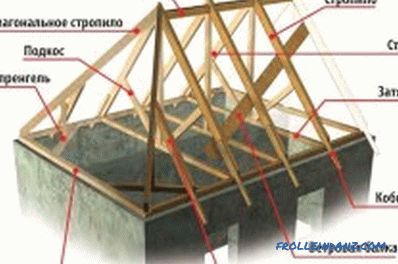
Elements of the truss system.
These two parameters — sections and length — do not always correspond to the desired parameters, and it is necessary to strengthen or lengthen the structure. Increasing the cross section of the truss system is called rafter buildup, and increasing the length is splicing rafters along the length. It is performed if you want to increase the length of the rafter legs.
Despite the similarity in the names, these are two completely different construction operations. Raising rafters is when some kind of, most often vertical, structural element is strengthened, joining together two boards or boards of the same length. Simply put, to increase - is to combine two identical elements into one to enhance its strength. When splicing, the elements are extended by interconnecting the ends of pieces of the same diameter so that their total length corresponds to the calculated length of the rafter legs.
Basic rules for joining rafter legs
The rafters are elongated with a hem with additional fixation of the junction with bolts, nails and (or) brackets. Cutting should be done so that the two pieces of the rafter fit as closely as possible to each other. If you have a choice, you should always choose the easiest way to cut. The point of the cut must be additionally fastened so that it can withstand all the loads and, if necessary, strengthen it with a metal fastener.
Splicing of rafters can be done in 3 ways: butt-joint, splicing "oblique prirub" and lengthening overlap. The final choice of the method is done directly during the installation of the truss system. When choosing, it is necessary to take into account the qualification of the splicing material, the available building material (board or bar) and the type of roof (pitched, semi-hipped or hipped). Regardless of the method chosen, tools will be needed to extend the rafters:

Tools for splicing rafter legs.
- ax;
- saw;
- crosscut;
- bow saw;
- hammer;
- kiyanka;
- planer;
- sherebel;
- chisel;
- chisel;
- manual or electric drill set of drills.
Despite the rather impressive list of tools, there is nothing too complicated in the merging process itself.
For butt splice, the joined ends of the bars or planks are cut at an angle of exactly 90º. Lining plates with a minimum length of 50 cm are fastened at the junction of the ends on both sides. The plates are fastened with nails in a checkerboard pattern - at least 8 nails per pad (four in each of the ends to be joined). Recently, nails are increasingly being replaced with long screws, or, if the ends of the boards, which have been bolted to the nuts with metal plates, are joined.
Important detail: to protect the junction from accidental lateral loads at the ends of the parts to be joined, holes are drilled into which the iron pin is inserted. A simpler, but also more time-consuming method - docking with a spike.
Splice joining of rafter legs.
With this method, a spike is cut at the end of one part, and a groove is carved at the end of the other. Inserted into each other, they, like the iron pin, will prevent lateral loads.
In order to make the rafter "obliquely cut", the adjoining ends of the parts of the rafter are cut at an angle of 45º, after which the cuts are stacked on top of one another and fastened in the middle of the joint with a 12 or 14 mm bolt. To do this, a through hole is drilled at the attachment point, the size of which should correspond to the bolt diameter. If the hole is larger, a gap will appear in the attachment point, creating additional strain on the deflection.
The technique of extending rafters overlapping implies overlapping one part of the rafters to another at least 1 m, then, as in the case of the “butt” method, the connected elements are fastened with nails in a checkerboard pattern. Sometimes for fastening use metal hairpins on which from both ends tighten the nuts and washers. This method is good because you do not need to observe perfect accuracy at the ends of the elements to be joined.
Lap joints are more often used when boards are used as truss feet. The connection in the "oblique prirub" is usually used for the elongation of the beam of large cross section. A butt joint can be used in both cases.
With any method of splicing, the place of joining becomes a kind of plastic hinge.
But since the rafter must be uniformly rigid along its entire length, splicing should be done at a distance not exceeding 15% of the span length from the support point on which the rafter is installed (run, tiller or intermediate support) . In this case, the deflection of the rafters at the junction will be as close as possible to the zero mark.
Paired and composite rafters
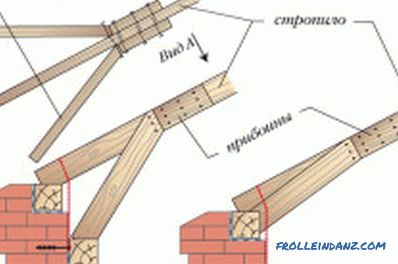
Strengthening system for rafter systems with additional struts.
These two types of rafters made of planks are lengthened quite often. For their extension, the overlap method is usually used. Paired rafters are made of two or more boards that are connected by wide sides and stitched together in staggered nails.
In order to increase the length of such a rafter, it is joined to the same paired system. In the case of docking, one board in each system must protrude at least 1 m above the other, and it is these boards that are fastened together. This method of docking allows you to create a robust overall design of rafter legs, not inferior in strength to the rafters of solid timber, which allows the use of such rafters in the device hip and poluvalmovyh roofs.
For composite rafter, three boards are needed. Between two boards of equal length, the third one is laid, the same width as the first two. And it does not fit the entire length of these two boards, but enters them for at least 1 m, but usually, for greater reliability, such an entry is made on a third of their length.
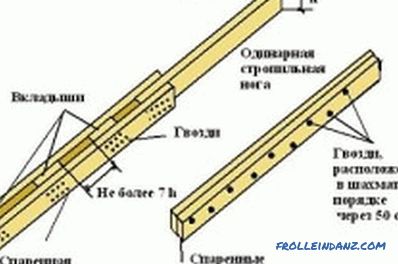
Scheme of options for rafter extension.
The result is a truss foot, on the one hand consisting of two boards lagging behind each other, and from the other side from one that is in the middle between the first two. The location of the board between the two is stitched in staggered nails or bolts.
In the remaining gap between the two boards, inserts are inserted from trimmed boards, equal in width and thickness to the insert liner, and fastened with nails, and in these places it is not necessary to observe the checkerboard mounting order. The length of such liners should not be less than double the width of the boards. Install such rafters single board on the girder, and double - on the power plate.
But still, composite rafters are significantly inferior to paired rafters for durability and reliability. This type of roof system can safely be used for the construction of pitched roofs, but for hip and semi-hinged types of roofs their use is undesirable.
If during the construction of the roof there is a need to extend the rafters, there is no need to call the professional craftsmen. This job is quite capable of anyone who knows how to handle an ax, a plane and a chisel. The main thing is to do it slowly, but correctly, than quickly, but anyhow. And then you will have a solid and reliable roof, and the construction of the rafters you have created will serve you faithfully for more than one decade.
Good luck! Reliable roof for your home!
Didn't find the answer in the article? More information on the topic:
-
Features of the device for flooring on wooden beams
The device of a floor on wooden beams is 1 of 2 possible variants of its construction. Floor beams are important structural elements of the structure. To lay the floor on them need to special rules.
-
Wooden house: do-it-yourself process
How to build a wooden house with your own hands? Choose a suitable project, purchase materials and tools and, following the recommendations, start construction. Recommendations further.