The roof is the most important part of the house. It defines both its external (architectural) appearance and operational qualities. Various types of roof systems allow you to implement almost any version of the roof design that best meets the requirements of the developer.
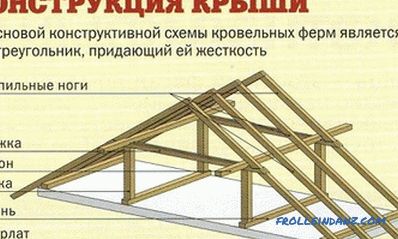
Roof construction.
Requirements for the roof system
During the life of the roof, various factors affect the roof, the most significant of which are:
- snowfall;
- wind;
- seasonal fluctuations in temperature.
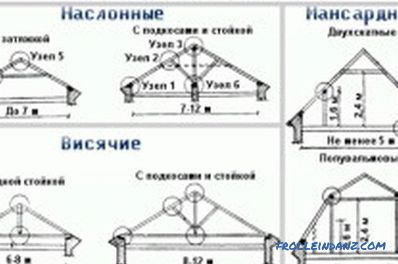
Types of roof truss systems.
The most common material for the manufacture of parts and assemblies of truss structures is wood. When designing, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of damage to building material by insects and microorganisms during operation. Impregnation of wooden parts with antiseptic solutions and the use of constructive measures to create favorable operating conditions will help eliminate the effect of biodeterioration.
The constructive measures include:
- use of vapor barrier from the attic space;
- inadmissibility of direct contact of wooden parts with masonry or massive metal elements;
- providing high-quality waterproofing roofing carpet.
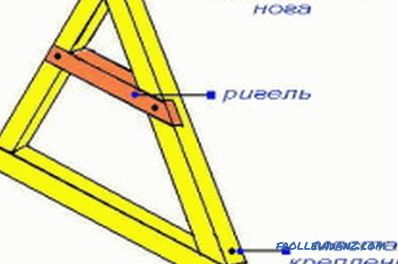
Elements of the roof truss.
The impact of the snow load is compensated at the design stage by selecting the required sections of structural elements. In climatic areas with a significant level of snow cover, it is recommended to reduce the distance between the rafter beams and increase the angle of the roof.
Increasing the angle of inclination, in turn, can lead to an increase in the windage of the roof. In areas characterized by the presence of strong and prolonged winds, this factor can lead to both local destruction of the roofing carpet, and to more large-scale damage.
Under the influence of seasonal fluctuations in temperature, the building materials of which the roof and supporting structure are made will expand or contract. The degree of temperature deformations is characterized by a coefficient of thermal expansion. Accordingly, different materials under the influence of seasonal fluctuations in temperature will be deformed to varying degrees.
Under unfavorable circumstances, there may be a violation of the integrity of the roof covering or even the appearance of cracks in the supporting elements of the truss structure. The best option is the selection of materials with approximately the same value of thermal deformation.
Elements of the truss
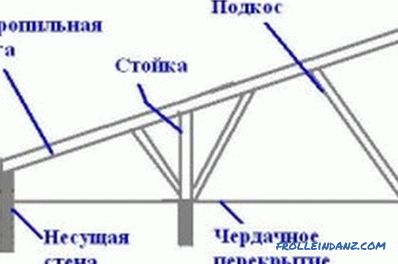
The design of the shed roof system.
The truss system supporting the roof consists of several elements:
- truss beam;
- power plate;
- tightening;
- bolt;
- ridge bar;
- brace;
- rack;
- lying.
The rafter is the main element of the system. On it fastening of an obreshetka for the roof device is made. Most often as rafters used wooden beams or thick boards.
Mauerlat is a timber fixed on the upper edge of the wall and used to secure the lower edge of the rafters and transfer the load to the walls. When building a frame house or a log house, the role of the mauerlat will be performed by the upper trim or the upper crown, respectively.
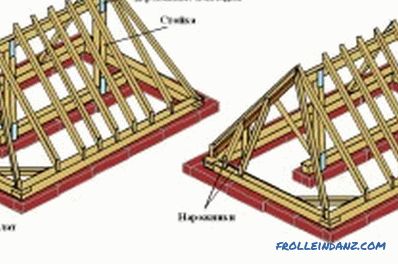
Diagram of the truss system of the hip roof.
Additionally, in order to compensate for the bursting load transmitted to the walls, tightening beams are used. They can be top location (bolt) and bottom (puff). Very often, puffs simultaneously perform the function of interfloor overlap.
With significant loads on the roof to give it additional bearing capacity, the upper ends of the rafter legs are additionally reinforced with a ridge bar.
Significant overlapping span sizes necessitate the use of additional struts. Vertical posts are installed under the ridge bar. To strengthen the rafter legs, struts can be used, which are cut at one end into a rack or by pulling, and the other into the rafter. The cutting of the strut is allowed at any angle, but the most frequently used angle is 90 °.
Perpendicular to the puffs can be installed lying - beams, which serve as a support for vertical racks. In some cases, logs can be used as a base for the struts.
In practice, in the design and construction of buildings, two main types of roof systems are used: hanging and mounted.
Suspended rafters: features
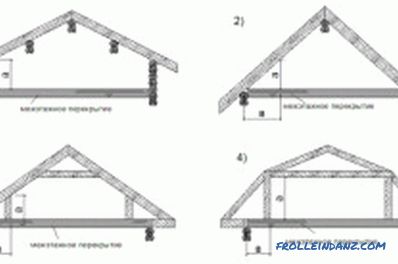
Common forms of mansard roofs.
The roof construction using hanging rafters is used to block spans up to 6 m. With this design, the lower part of the rafters rests only on the outer walls, while the upper parts rest on each other.
In the simplest case, such a system consists of two beams fastened with upper ends. In the lower part of the beam based on the mauerlat. For such simplicity of construction, one has to pay with large amounts of holding loads that the rafters will have on the walls. To compensate for the load can be due to the installation of bolts and puffs.
In order to cover spans that are longer than 6 m, it is necessary to install additional vertical pillars and struts resting on the top. The length of the section of rafters between the mauerlat and the cutting of the strut in this case should not exceed 4-4.5 m.
Additional subrafter structures will inevitably lead to an increase in the weight of the entire truss system. With a significant increase in weight, problems may arise related to the bearing capacity of the foundation or the structural strength of individual elements of the building. As a result, you will have to use lighter roofing materials than previously thought. This can be quite difficult.
Inclined rafters: characteristics
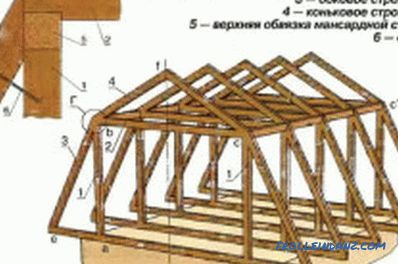
Diagram of the truss system of a sloping roof of the attic.
Suspended truss systems differ from hanging ones by the presence of intermediate support points, which can be used as internal capital walls or columns. Thus, there are at least three points of support - two external walls and one internal wall or column.
The use of intermediate points of the supports allows to reduce the actual length of the span to be covered and to reduce the cross section of the structural beams.
An important point that must be considered when designing a floor system is the inverse relationship between the angle of the roof and the pitch of the rafter legs. In other words, the greater the steepness of the roof, the more often it is necessary to install truss beams.
Combined roof system
Overlapping significant spans requires the use of roof trusses.

The installation scheme of the truss system: A - the attachment of rafters to the power plate; mount the fillies; B - a general view of correctly made rafters; B - stretching and strut; G - correct fastening of the skate; D - fastening to the strut; E - rafters in the assembly.
Such trusses use in their construction the characteristic elements of both systems and are a combined truss system.
Most often such a system is used for the manufacture of roofs of the so-called mansard type. The walls of the room on the second floor will be formed by vertical posts, which are at the same time intermediate points of support for roof beams.
Horizontal bars running along the top of racks (girders) will simultaneously perform the functions of a ridge bar for side roofs and a roof plate for upper skates.
The part of the truss truss that connects the upper ends of the uprights performs the function of the crossbar for the side ramps and at the same time is the tightening for the upper part of the truss.
Additionally, to enhance the strength of the structure, struts can be installed that fasten the vertical posts and rafters of the side slopes of the roof.
The combined truss truss is somewhat more difficult to manufacture than traditional types of truss systems. However, the laboriousness and complexity of manufacturing is more than compensated for by the absence of the need for additional supports when covering large spans and increasing the bearing capacity of the roof.
Didn't find the answer in the article? More information on the topic:
-
What types of lumber exist?
Types of sawn timber: according to the method of processing raw materials, sawn timber is divided into unedged and edged. Depending on the processing method, the materials may be called unmilled or milled.