Wood still remains an extremely common building material, from which not only individual elements of buildings, but also entire buildings are made. Wood can be attributed, and materials made on its basis, so they all relate to wooden structures. It is known that the main drawback of wood is its high fire hazard, therefore impregnation of wooden structures with flame retardant is the best way to protect a building from fire. How many fires could have been avoided if flame retardants were used to treat wood structures.

Wood impregnation with a flame retardant is the most common and cost-effective method of fire protection of wooden structures.
What is a fire retardant?
Fire retardants are chemically prepared compounds that are designed to prevent wood from burning. The name is derived from the Greek "anti" (against) and "feast" (fire). The wooden construction sufficiently impregnated with flame retardant is able to counteract the fire impact for a much longer time. The flame retardants do not have a high melting point, so they begin to melt much earlier than wood can ignite. It is in this way that the flame retardant impregnation creates a barrier between the wood and the ignition source for oxygen supporting the combustion.

Wood antiseptic scheme to protect a wooden house.
It can be noted that the fire partially acts "to its own detriment" by heating the impregnation, in which chemical reactions that prevent its spread are activated.
As a rule, the main components of compounds for the treatment of wooden structures are flame retardant chemicals that differ in low melting point, derivatives of boric, silicic or phosphoric acids. In addition to the creation of a film, flame retardants affecting the flame triggers the reaction of the release of gases that prevent combustion. Volatile substances formed during the melting of the flame retardant layer displace oxygen from the zone of contact with the wood.
Classification of fire retardants
Fire protection of wooden structures is divided according to the processing method into 2 basic types:
- impregnations;
- coatings.
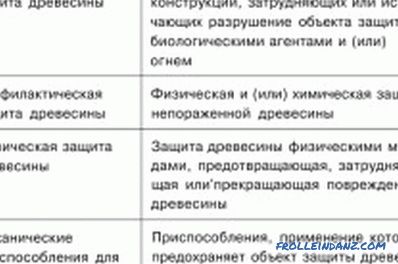
Table of definitions of wood protection terms.
Coating materials include various primers, pastes, paints and varnishes. In most cases, they are easier to apply already in the process of building operation. But such a flame retardant does not penetrate deep into. Someone does not like the fact that the paint covers the surface structure characteristic of wood, that is, it depersonalizes it. Because of this, protective coatings are often applied to areas hidden from sight.
Another type of protection for wooden structures is impregnation. For those who do not want to deprive themselves of the pleasure to consider the structure of wood, penetrating solutions - ideal. In turn, impregnations are water or organic soluble. Oddly enough, but the latter are made on the basis of solvents capable of ignition. In addition, these solvents are harmful to health, so the processing of wooden structures with organosoluble compositions is mainly carried out under production conditions.
Most owners of wooden structures prefer to use water-soluble impregnations, but they are effective only where the wood is not exposed to prolonged moisture. Nevertheless, these formulations are divided into several categories:
- nonwashable;
- difficult to wash;
- washed out;
- lightweight.
For internal processing, consumers prefer to buy impregnations of the last 2 categories.
When producing flame retardants, the manufacturer tries to make them a universal means for protecting wood. In addition to its main function, the compositions often act as antiseptics.
Processing of structures
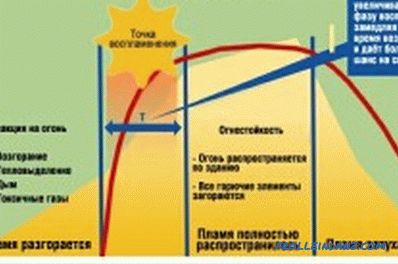
Fire development scheme in a building, the supporting structures and elements of which are impregnated with a flame retardant.
Fire treatment of wood with formulations can be deep and moderate. In living conditions it is almost impossible to carry out deep impregnation, since work to improve the fire resistance of wood is already being carried out in the erected structure. Of course, there are compounds that have high penetrating properties. But with moderate processing, we can talk only about the relative depth of their penetration into the body of wood.
Work to improve the fire resistance of a building is carried out either by spraying wooden surfaces or by applying a brush to formulations. It is necessary to add that the processing of wood outdoors should be carried out only during the warm season, since at low temperatures the frozen moisture in the thickness of the wood prevents the penetration of the flame retardant into the depths.
Standardization of fire retardants
Only those compounds whose efficacy corresponds to groups I and II are flame retardant. GOST determines the effectiveness of fire protection as the mass loss of the material treated with a fire retardant when exposed to fire. If, during fire tests, the processed sample lost no more than 9% of the mass, then the flame retardant is included in Group I. The wood impregnated by it is called flame-resistant. Group II includes impregnations, with which the sample loses no more than 1/4 of the mass during combustion. The wood they treated is flame-resistant.
All flame retardant impregnations and coatings are subject to mandatory certification, which is carried out by units of the Ministry of Health and Social Development.
The bodies of the ministry, according to the results of the audit of the enterprises for the production of fire retardants, issue a sanitary-epidemiological conclusion. A negative assessment of the Ministry of Healthcare and Social Development deprives the manufacturer of the right to a certificate, and products that do not have documentary evidence of its quality by the state cannot legally be produced and applied. The flame retardants that meet all standards are certified by the PozhTest organization of the FSI VNIIPO EMERCOM of the Russian Federation. It is necessary to add that the specialists conducting the processing of wooden structures with flame retardants must have an appropriate license.
Didn't find the answer in the article? More information on the topic:
-

How to dry a tree qualitatively?
Recommendations on how to dry the tree yourself. Rules for proper drying of wood. Drying under atmospheric conditions. Advice of experts on drying wood.
-
Proper storage of lumber
Storage of lumber must be correct. It is best to store boards in stock. The material is laid on special lining bars. Laying on the ground is strictly prohibited.
-

How is wood waxing done?
Step by step instructions on how to wax wood. Useful tips and tricks, materials and tools for work. How to prepare the surface? How to apply wax properly?