The huge variety of currently available outlets is due to the multitasking of these elements of the electrical network. Specific conditions for their use dictate certain requirements not only to their appearance, but also to functional parameters. This article describes in as much detail as possible all types of sockets available today, having studied the features of which you will receive comprehensive information regarding the design differences and principles of operation of devices intended for plug-in connections.

Types of socket outlets
Depending on the country in which certain standards are legally fixed, sockets differ in the number of contact elements, as well as their forms and sizes. In addition, each device has a letter designation, approved at the end of the last century by the US Department of Commerce. The classification proposed by the Americans was approved by other countries, and is currently valid worldwide:
Type A

A - the standard, which at one time was ubiquitous in North America. Following the US, it began to be used in 38 countries. This type consists of two non-grounded flat contacts arranged in parallel. Grounding element in this case is not provided. Today, such devices can still be seen in many old buildings, since they are all compatible with the modern type of plugs. Certain differences have the Japanese standard, which provides additional requirements for the parameters of the enclosures of products.
Type B

B - an improved version of the American standard, supplemented at the bottom of the design with a long round contact providing grounding. In addition to the United States, these types of electrical outlets are used in Canada and Mexico. In addition, they are found in several countries in South America, including Colombia, Ecuador and Venezuela.
Type C

C is the most common standard in Europe. The so-called euro socket, consisting of two round contacts, is used, including in the CIS, as well as in the Middle East and in most countries of the African continent. Grounding in this design is missing. In the Russian Federation, the sizes and safety requirements for such products are defined by GOST 7396.
Type D

D - an outdated standard previously used by the British in territories belonging to the British Empire. At the moment, sockets with three round contacts, located at the tops of the triangle, are mainly used in India, and are also found in old houses of other countries, where the British once had a hand in arranging power supply lines.
Type E
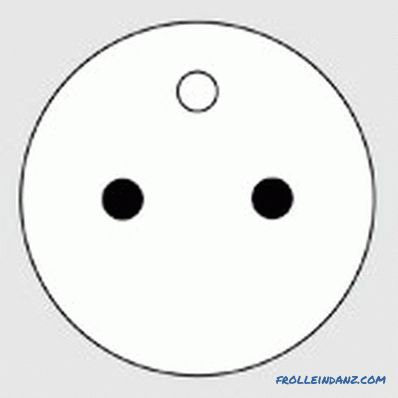
E is a modern French standard that differs from the type With the presence of a grounding contact, which is located at the top of the device. Similar elements of the power grid are also used in Belgium and Poland. At one time they were introduced in the territory of the former Czechoslovakia.
Type F
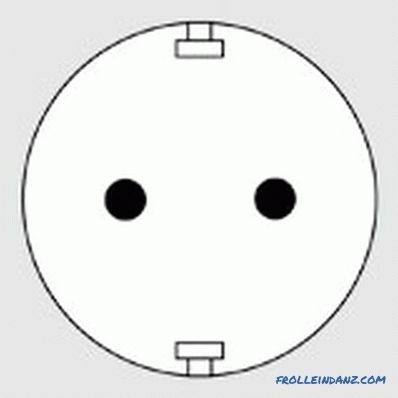
F - the European standard in the form of a design from two round contacts, supplemented from above and bottom grounding brackets. Initially, such devices appeared in Germany and began to be used for alternating current. These types of sockets and plugs are also called "Schuko", which is an abbreviation of the German Schutzkontakt, literally meaning "protective contact". Products are fully compatible with the plugs of Russian and Soviet production.
Type G

G is the British standard providing a fuse, located inside the plug. The device consists of three flat contacts, two of which are located below, and one - in the upper part. It is allowed to connect evrovilok through a special adapter, which must also be embedded fuse. This type of power grid elements is supported in Ireland, as well as in the territories of some states that were once British colonies.
Type H

H —The Israeli standard is three round contacts (until 1989, flat elements), forming their location the Latin letter Y. This type of connection to the electrical network is unique because it is used exclusively in Israel. Other types of sockets and plugs are completely incompatible with it.
Type I
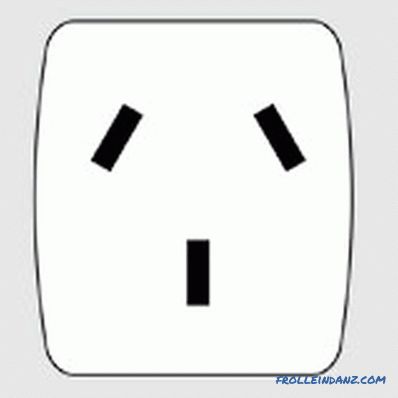
I is a standard common in Australia and New Zealand. Two flat contacts are angled. The third is vertically located at the bottom and is the grounding element. Similar types of electrical outlets are used in Papua New Guinea, as well as in the Republic of the Fiji Islands.
Type J
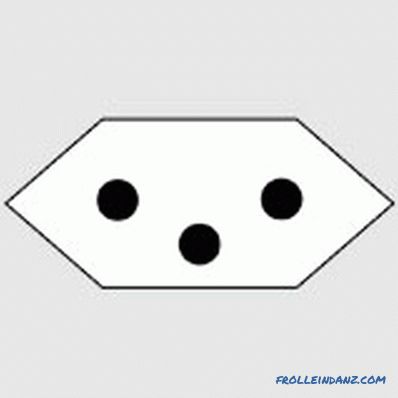
J is a Swiss standard that has a certain similarity with type C, but characterized by the presence of a grounding contact, set aside. When connecting Evrovilok no need to use adapters.
Type K

K is the Danish standard, the only difference from which French type is the location of the grounding pin installed directly in the plug, and not in the design of the outlet.
Type L
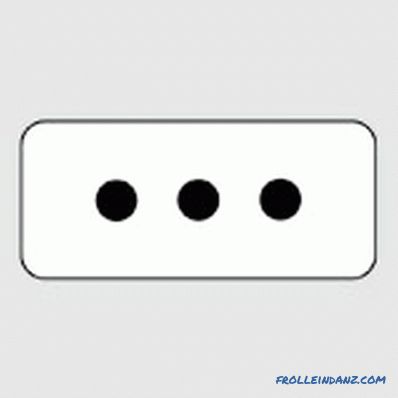
L is an Italian standard that assumes compatibility with type C euroorowers. The design consists of three round contacts forming a horizontal row.
In some cases, old British samples, still used in South Africa, may be indicated by the letter M.
Technical specifications of the sockets: voltage and frequency
According to European standards, the voltage in the power grid is usually 220-240 or 380V. Sockets designed for 220 volts are usually used to connect various electrical devices whose power does not exceed 3.5 kW. This limitation is due to the inability of standard devices designed for low-power household appliances to cope with current strength beyond 16A.

For more powerful electrical devices it is recommended to use industrial three-phase sockets for which the permissible current is 32A. Such products are rated for 380V.

In addition, for certain types of sockets, a certain frequency of alternating current is provided, which is 50 or 60 Hz. The most common European standard, including that used in Russia, is designed for the first option.
What are the sockets according to the method of installation? The version of the housing in this case depends on the type of wiring. Built-in sockets
Built-in products involve the installation of the pads, on which the contacts are located, in a special box (power socket) hidden in the wall. As a result, only the protective housing of the device, slightly protruding above the surface, is within sight. For electrical networks with grounding, sockets are used that are equipped with additional grounding contacts.

Surface-mounted sockets
In cases with external wiring, surface-mounted structures are fixed to the wall surface. Contact elements are located under the body of the product, completely hiding the connector.

There are rather original types of electrical outlets of the surface type, the installation of which consists in fixing the device on the baseboard that hides the wiring laid under it. In Russia, they are not particularly popular, since they are completely out of tune with modern interiors, and often break down as a result of mechanical effects.

Portable sockets
Portable sockets are often equipped with a cord with a plug, which allows them to be used as extension cords. However, there are also models without a cord that are connected directly to the cable that is led out of the wall. During installation, you must divide the device into two parts, loosen the construction screws, then clean the contacts and insert them into the clamping terminals. Some portable products are equipped with a power button and an indicator indicating the operating mode.

Number of used sockets in the modular unit
Double socket
The device, which has two electrical points, allows you to simultaneously connect to the network different devices. The basis of such a product is a block, made in accordance with the standard dimensions, so that no additional floorplate is required. Structurally, the differences between the types of socket blocks are solely in the number of seats. The internal space of the housing is divided into terminals, each of which contains contacts and terminals.


Triple Socket
In cases with open wiring, it is recommended to use a waybill for attaching a receptacle unit for three energy consumers the block.

For a closed electric power line, a frame with the appropriate number of sections is used. An outlet can be inserted into each section, resulting in a block consisting of three sockets.

Fourth socket
In most cases, one-pin devices are used to install four or more points. For mounting a frame with the corresponding number of sections is used.

Sockets with additional functions
There are models of sockets, in which besides the main components, there are special electronic or mechanical components, which are assigned certain functions. Different types of electrical outlets may have certain features that we will look at next.
Sockets with built-in RCD
Designs with built-in RCD are designed to connect powerful electrical devices. Mostly they are installed in the bathrooms, because with an increased level of humidity in the room increases the risk of electric shock. Thanks to the protective shutdown device at the time of leakage, the built-in relay is triggered, which opens the input contacts in time. This allows not only to prevent damage to the appliance, but not to cause harm to human health.

Sockets with curtains
Models with curtains, which are often called “child protection sockets” in everyday life, are equipped with special panels that hide the input sockets. Access to the contacts in this case is possible only at the moment when the plug enters the holes. In fact, the task of the shutter is to prevent any foreign objects from entering the outlet. This is the perfect option for a child's room.

Sockets with covers
Sockets with covers are mainly used in rooms with high humidity. In this case, the protective elements prevent not only the ingress of water, but also dust inside the device. Additional mechanisms are mounted with special clamps and screws.

Sockets with a timer
The model with a timer allows the user to independently set the time period after which the power supply to the device will be terminated. These types of sockets are quite convenient to use when operating heaters that are not equipped with their own automatic shutdown system.

Sockets with an electric meter
Designs equipped with a built-in electricity meter make it possible to control the consumption of energy consumed by a particular household appliance. The indicator on the case changes its color based on the power of the connected device.

Sockets with a fork ejector
A model with a fork ejector is a great option for those whose socket is not firmly fixed in the bottom of the plug. The presence of an additional mechanism allows you to gently pull out the plug, without making much effort.

Sockets with backlight
Socket with backlight, designed for use in conditions of insufficient visibility. It allows even in complete darkness to quickly find a place where you need to connect a particular electrical device.

Sockets with USB output
Products equipped with USB output. These are modern models of sockets with which you can charge a mobile phone, camera or other device at any time.

Socket with WiFi module
A power socket with a built-in WiFi module allows you to control devices used in your home using a smartphone or tablet. Inside this device is a microprocessor adjustable at a distance, which is responsible for the supply of electricity.

Special-Purpose Sockets
There are sockets designed for strictly defined purposes and structurally different from ordinary devices. These include:
Through sockets , which are intermediate elements in the electrical circuit. In this case, the power wire is connected to the contacts, which does not end there, but is sent to the next device. Such types of electrical outlets are used, as a rule, in the boxless dilution method.
Shield connectors for use in distribution boards and installed using special metal strips equipped with snap-in mechanisms.

Antenna socket, equipped with a special connector that is compatible with the tip of the television antenna cable.

A socket for connecting to the Internet , which can also connect several computers that interact with each other. It differs from other types of devices in the number of contacts and the structure of the socket for the cable tip.

Protective properties of various sockets
The degree of protection of various types of sockets from touching, as well as the ingress of certain parts of solids, particles of dust and moisture, is indicated by IP marking, where the first digit corresponds to the following indicators:
- 0 - total absence of protective functions with open access to equipment nodes;
- 1 - limited the penetration of large solid bodies with dimensions of more than 5 cm.Protection against the touch of fingers is not supposed;
- 2 - protection is provided for the fingers, and the object size from 1.25 cm;
- 3 - device nodes are protected from possible contact with power tools and other foreign objects larger than 2.5 mm;
- 4 - indicates the presence of protection preventing ingress of solid particles having dimensions more than 1 mm;
- 5 - indicates partial protection against dust;
- 6 - the highest degree of protection against ingress of any foreign objects, including microscopic dust particles.
The second digit of the marking indicates the degree of protection of the device against moisture. "0" in this case also indicates the absolute insecurity of the equipment. Other designations can be seen in the following examples:
- 1 - vertically falling drops will not cause a short circuit upon contact with the shell;
- 2 - drops that fall vertically at an angle of no more than 15 degrees will not be able to overcome the shell;
- 3 - protection prevents closure even in cases where water drops fall at an angle of 60 degrees;
- 4 - equipment components are reliably protected from moisture, regardless of the direction of movement of the spray;
- 5 - water is allowed to enter without being under pressure it. The devices having such a designation can be regularly cleaned;
- 6 —the equipment is able to withstand sufficiently powerful directed water flows;
- 7 —the device can be briefly immersed in water to a depth of no more than 1 meter;
- 8 - immersion to a considerable depth is allowed;
- 9 - absolute tightness allows the equipment to operate under water with unlimited duration.
The "NEMA" standard marking is used for types of electrical outlets manufactured in the United States and certified. Below are the areas of use of devices with different indicators "NEMA":
- 1 - the products are intended for installation in residential and administrative premises and provide protection against ingress of dirt;
- 2 - designed for domestic premises where there is a probability of moisture ingress in minimal quantities;
- 3 - devices used outside buildings in conditions of increased dust formation, as well as atmospheric precipitation. Additional characteristics have the models "3R" and "3S";
- 4 and 4X - equipment capable of withstanding the dirt splashed as a result of traffic, and also resistant to aggressive weather conditions;
- 6 and 6P - the sealed enclosure provides protective functions, thanks to which the device can be placed under water at relatively shallow depth;
- 11 - products are mainly used in places where corrosive processes constantly occur;
- 12 and 12К - calculated on eniya with elevated levels of dust
- 13 - are particularly resistant to various kinds of pollution, including oily substances.
There are also other types of markings, which, for example, indicate the degree of strength of the body of the product. However, to consider this indicator in relation to the ordinary household outlet does not make sense.