In the large territory of our planet in winter, minus temperatures are observed at which water freezes in the ground, to a depth determined by the cooling level. With a decrease in air temperature, the freezing rate increases. This factor is of great importance in construction, as it partially determines the level of laying the foundation of the house, as well as laying pipelines that transport water. There is a concept of the normative depth of soil freezing. This value depends on the geographical location of a particular territory. To determine this indicator, long-term observations were carried out, according to which the average values of the temperature regime were recorded. It should be noted that the definition of this indicator was carried out in the absence of snow cover.
Differences between the depths of freezing
In practice, the real value of the parameter and the normative value indicated in the normative-technical literature differ from each other.
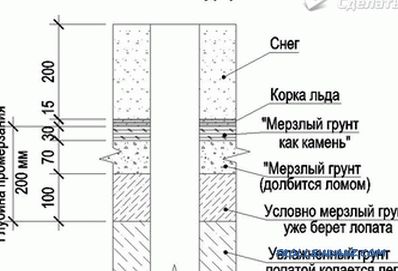 How does the soil freeze through
How does the soil freeze through
- The fact is that virtually the entire territory of Russia and many In other countries, a long period of time is under the snow cover, and it significantly reduces the depth of soil freezing. In addition, when it is present, the humidity index also increases, and it also affects this parameter.
- When building a house to live, not only in the warm season, but also in the cold period, of course, the heating system is arranged. This factor also affects the mark of soil overcooling - it will be much higher than the standard mark. At the same time, in the conditions of construction of a summer house, in which it is planned to live only in warm, comfortable weather, this difference will not be of fundamental importance. In order not to deepen the foundation, you can take advantage of new technologies existing in construction. To do this, around the perimeter of the house you need to put any suitable insulation that protects against hypothermia, thus, eliminating the need to carry out extra construction work. Thanks to this technological reception, the ground will be insulated and the level of the base of the foundation can be raised higher than allowed by the value of the standard depth. Thus, it will be possible not to be afraid that in the winter there will be a deformation of the base of the building. For greater reliability in the construction of the house, you can apply the strip foundation, which is a foundation of reinforced concrete. This design evenly distributes and absorbs the load; it is a reliable and relatively simple structure. The tape type of the base, with a stable depth of freezing, can be made shallow.
During the construction of a heated residential building, the estimated depth of frost penetration will be less than the standard depth of approximately 10 to 30%, depending on the type of floor.
 Irregularity of freezing
Irregularity of freezing
After the above information, you can think about whether snow removal is beneficial or detrimental. On the one hand, this event will relieve the cleaned area from flooding during the thaw, on the other hand, the cleared areas will become bare, which means they will be more susceptible to penetration into the ground below-zero temperature. The presence of snow in this case is a useful phenomenon. In order not to be blown away from certain territories, it is possible to plant shrubs on the site that prevent soil from being exposed in frosty weather.
Seasonal frost penetration
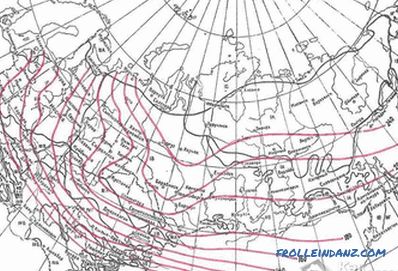 Map
Map
In different territories located in different zones, seasonal freezing of the soil is determined according to SNiP 2. 02. 01-83 *. Experts have been observing for many years and determined the average values of this parameter. According to clause 2. 27, the depth of soil freezing can be calculated using the formula:
dfn = do ∙ mt, where
do is a coefficient depending on the type of soil.
With clay and loam, do = 0.23, sandy loam and fine sand - 0.28, gravel sand and grain size above the average - 0.30, coarse-grained soil - 0.34.
mt is a coefficient that is determined by summing up the highest monthly average values of sub-zero temperatures during the winter period for a specific area. To determine it, you need to use the table 3 SNiPa 23-01-99 *.
From the formula it is clear that the type of soil affects the mark of soil freezing. For each of them is taken its own individual coefficient. If the depth of soil overcooling exceeds the level of groundwater, this fact must be taken into account during construction. Water in freezing weather will freeze, increase in volume and put pressure on the soil. Under the influence of ice, the soil will move and act destructively on the foundation. For this reason, the main house must be built below the depth of freezing.
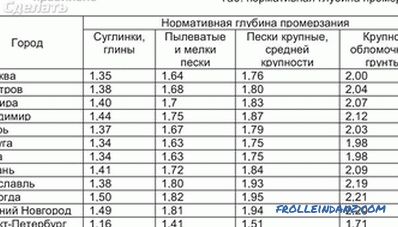 By city
By city
For example, the seasonal depth of soil freezing in the Leningrad region is 1.20 m in the Moscow region - 1.40 m.
Video




