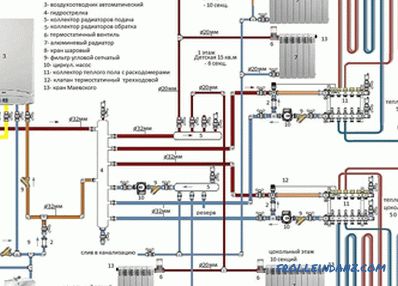
The owner of the future private house, when choosing a roof, often chooses an inexpensive option with two ramps. The practical and uncomplicated design of such a roof is reliable, durable and provides good protection against bad weather. Consider the structure of the rafter roof system - the most important element of its design.

About a gable roof in a nutshell
A gable is a roof in which two rectangular flat slopes are joined at the top at an angle. At the same time there are triangular openings on the sides. Gables are inserted there. To make the structure strong, reliable and serve for a long time, various retaining and supporting elements are used in it. The most important of them is the truss system of the gable roof, which, in fact, is the subject of this material.
Structural elements of dual-pitch roofs
In general, all these elements of gable roofs are boards, bars and beams of various lengths, shapes and sections. Consider them all in order.
Mauerlat
This is a coniferous square bar, the size of which is usually 10 or 15 centimeters. It is placed along each of the bearing walls, attaching to them with rods on the thread or anchors. The purpose of this element - a uniform transfer of load from the feet of rafters to the bearing walls.
Truss foot
This is a bar, in the section measuring 15 centimeters by 5 (or 10) centimeters. It is from such elements that our triangular contour of the roof is assembled, which bears the brunt of the wind, hail, snow, and other vicissitudes of weather. To adequately withstand these loads, rafter legs are arranged in steps of 0.6 to 1.2 meters. The more weighty the roof is supposed to be, the less this distance is. In addition, the step rafters, in some cases, will depend on the design features of the used roofing.
Legs
The square bar for this element has the same section as for the mauerlat - 10/10 or 15/15 centimeters. It is placed horizontally on the internal bearing wall in order to evenly distribute the load from the roof racks.
Tightening
This element is used for a hanging truss system. He completes the triangle truss legs, not allowing him to crawl away.
Racks
Bar for them is taken square, the same as for the previous element. Racks are placed vertically, taking the load from the ridge and passing it to the bearing wall inside the house.
Strutches
These elements play the role of a transmission link between the rafter legs and the bearing elements. Having connected a tightening and struts, receive a farm - very strong element. Even with a large span, the farm will endure all the loads.
Crate
Perpendicular to the feet of the rafters lay bars (or boards) of the batten. Transmitting the entire gravity of the roof to the rafter legs, this structural element additionally holds them together. It is preferable to arrange the crates to take edged bars or boards. But in the absence of the best, the unedged board will fit, but with the bark removed. Well, in the case of soft roofing (for example, shingles on a bitumen base), the crate is made solid. To do this, take moisture-resistant plywood sheets.
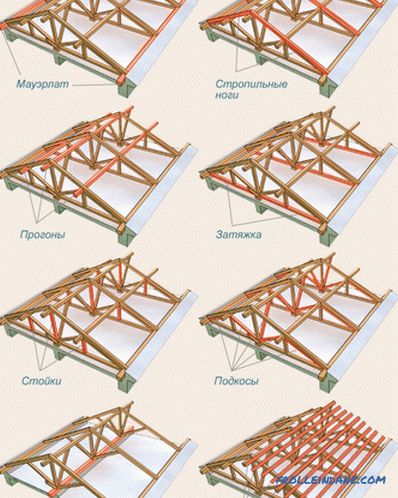
Ridge of the roof
Ridge is the upper place of the roof connecting the two slopes of the roof. It is formed by connecting the truss legs at the top of the roof. It is located horizontally.
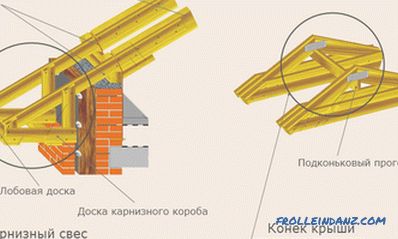
Roof overhang
This element, protruding from the walls at a distance of approximately 40 centimeters, does not allow rain flows to wet these walls.
Filly
And again the "horse" name. These structural elements of the truss system of a dual-slope roof are needed to organize a roof overhang. The need for them appears only when the rafter legs are too short, and there is not enough of them for the overhang. Then these legs are extended by filly, which are boards of a somewhat smaller section.
Types of roof systems of dual-slope roofs
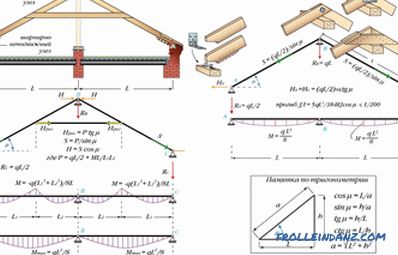
There are only two of these systems: the hanging type and the sliding type. The former are used when the outer walls of the house are 10 meters apart or less. There is one more condition - between these very walls there should not be a bearing wall that divides the house into two. Otherwise, use rafters. When a house under construction is divided not by a bearing wall, but by columns, two truss systems are mounted at once. The rafters, located at an angle, will rest on the columns, and the hanging ones will perfectly fit between them.
A truss system of a hanging type
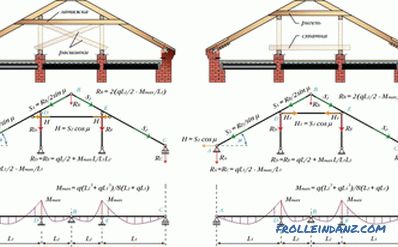
For this scheme of a truss system of a gable roof, it is characteristic that the rafters rest on the side walls. The bad thing is that this creates a bursting load that can damage walls over time. To prevent this from happening, the feet of the rafters are joined by tightening. As a result, a hard triangle is formed that is not subject to deformation under loads.Often, instead of puffs, floor beams are used, this is especially true when it is necessary to equip an attic space under the roof.
The advantage of this system is that it is not at all necessary to mount the power plate. In addition, it is quite easy to assemble those parts of the structure where the feet of the rafters rest on the walls. The board, laid through the insulating layer, will help to make the farm level and stable, providing a large footprint. Next, we consider the main types of hanging rafters. All of them are three-hinged.
# 1. A simple triangular three-hinged arch.
This is the simplest structure, which is a closed triangle, the two upper sides of which are subjected to bending stress. Tightening in such a construction does not work only in tension and is not a supporting structure, so it can be replaced with steel strands.
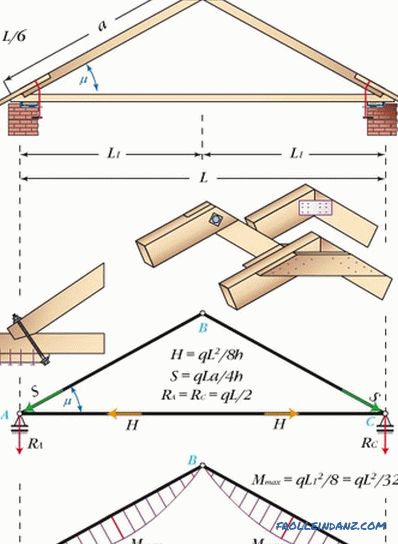
In this case, there are several solutions for organizing the structure of the cornice node. These are orthogonal frontal cuts, as well as the use of board or plate fasteners.
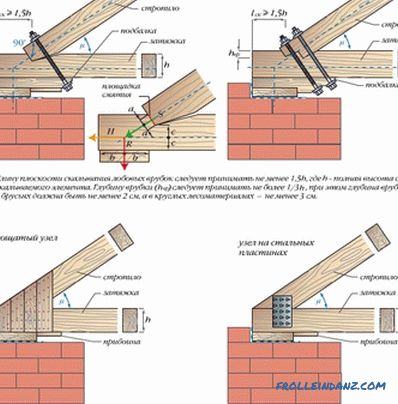
# 2. A triangular three-hinged arch, reinforced by the headstock or suspension.
This option was used only earlier, building large industrial or agricultural premises with a span of more than 6 meters. For private houses, this scheme is not suitable. Its principle is that the puff weight (made up of individual short elements) assumes the ridge. These elements are interconnected and with the suspension collar using a prub (oblique or straight). Bolts are used for fastening. Wooden pendant is called grandmother, and iron - heavy. This detail is hanging on the eaves node, and the fastener is attached to its lower part through wooden linings. Adapters are clamps that regulate the deflection of the inhaling, if it sags.
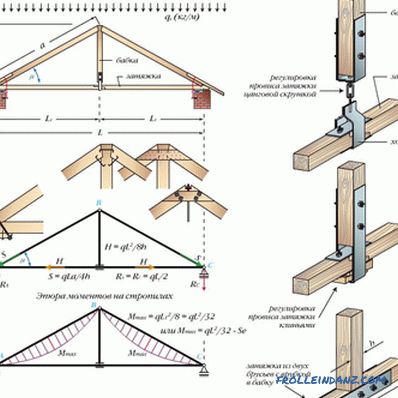
# 3. A triangular three-hinged arch with a raised pull.
If you want to equip an attic room under the roof, then this scheme is perfect. Here we stretch the banner not at the bottom, tightening the feet of the rafters, but at the top. Raising it higher, we increase the tensile load. Well, the rafters are held on the beams of the Mauerlat according to the principle of the ram. The load is uniform, and the system is stable. To do this, the edges of the rafters must protrude beyond the external walls of the house.
So that the puff does not sag, it is often balanced by a suspension. This is especially important if you plan to make a suspended ceiling or lay layers of insulation. With a short tightening suspension attached to the bolt and ridge, nailing two boards, with a long - make a few pendants. For heavy loads, clamps are used for fastening. They also combine, if necessary, two parts of the integral tightening.
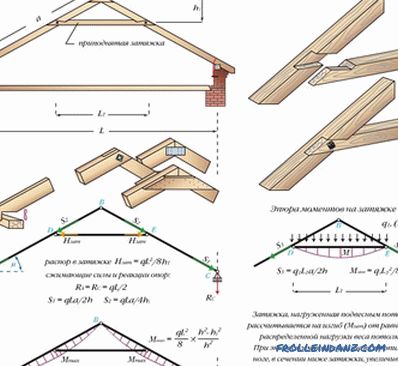
# 4. Three-hinged triangular arch with bolt.
Such a system is mounted in the event that the spacer loads are large. At the bottom is fastened, and in the upper part - the bolt. Due to this construction, the mounting plate against the wall is not necessary. In general, the bolt - this is the tightening, only experiencing the load not in tension, but in compression. The crossbar should not have a hinge to the feet of rafters, and then the design will stagger. If everything is done as it should, then the rafters will turn into continuous beams having three supports and two spans.
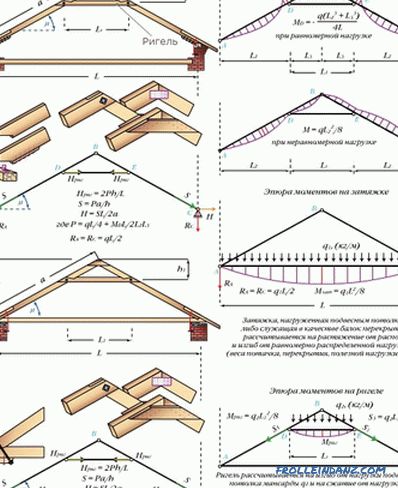
# 5. The three-hinged triangular arch with the headstock, complemented by struts.
About the system with the grandmother described a little higher. If the rafters are long enough in such a construction, they have to be propped up. To do this, and serve as a strut, reducing bending rafters load. There is no supporting wall for the hanging system, so it is necessary to rest the struts against the headstock. A stable rigid system takes the main load on its upper part, not bringing it to the bottom of the rafter. Tightening in this design is usually composite, connected by a prirub. Relying on the collar of the headstock, she pulls the ridge knot downwards. And he acts on the suspension and rafters, squeezing them.
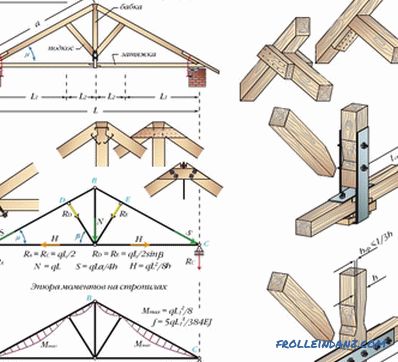
The rafter system of a nacelle type
This system has a vertical beam exactly in the middle. The weight of the entire roof through this beam passes from the ridge to the bearing wall. This wall is at an equal distance from the edges of the building. As already mentioned, the need for such a division of a building appears when the distance between its external walls is more than 10 meters.
# 1. Non-contoured slings.
In this design, the feet of the rafters are subjected only to bending, not pressing on the walls and not bursting them. There are three options for mounting such rafters, which solve the problem of loads on the walls of the building.
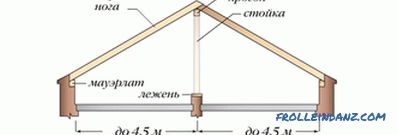
In the first version, the support for the rafter is either a mauerlat or hemmed with a special bar (support). For fastening the cutting with a tooth is used. The construction is insured with clamps or wire, which is a guarantee of the reliability of the construction. The upper part of the feet of rafters put on the girder girder.Fastening on the principle of sliding supports. Be sure to fix the holes in the upper part of the rafters.
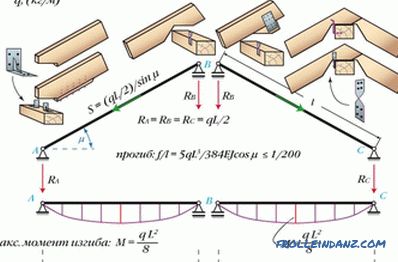
This is the most popular design. In it, the bottoms of the rafter legs are attached to the mauerlat by a movable joint of the type of a ram. It is also possible to mount with a piece bar. To keep the foot firm, we drive a nail in from above. Or you can attach a flexible plate of steel. At the top of the rafters, lying on the run of the ridge, either fix holes in pairs, or to the run (each of the rafters).
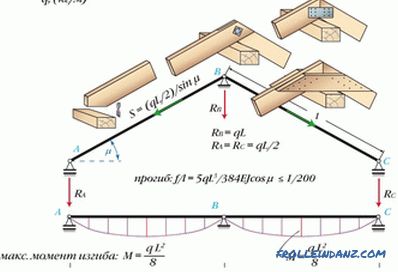
The peculiarity of the latter is that the rafters' legs and the ridge girder are rigidly joined into one whole. To do this, parallel to the ridge bar on both sides stuffed planks or bars. In this case, the beam is experiencing a strong bending load, but the legs of the rafters bend much less. This option is more difficult to perform than the second, so it is used less frequently.
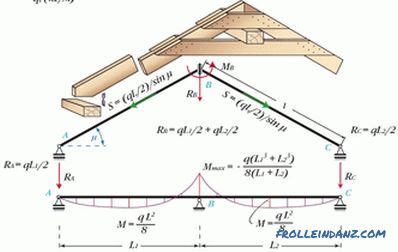
# 2. Spacer rafters.
In this case, the installation of a truss system of a gable roof is almost similar to the previous three options. There is one caveat: it is necessary to replace the attachment of the feet of the rafters from the movable one (like a slider) to a rigid, fixed one. And then the rafters will begin to transmit a bursting load to the bearing walls of the house. In general, such spacer rafters serve as an intermediate link from the inclined system to the hanging one. However, the difference in hanging rafters is that their run is not an essential detail. You can do without it.
For the spacer system, the mauerlat must be very tightly attached to the wall of the house. Yes, and the walls themselves must be thick and durable. You can use around the perimeter belt of reinforced concrete.
# 3. Rafters with struts.
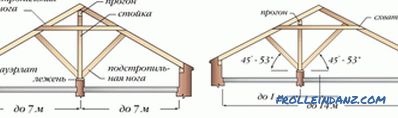
The strut, which, in fact, is the third foot of the rafter, is also called a subrafter foot. This third leg, working in compression, is placed at an angle of 45 degrees. In this way, it is possible to overlap even spans with a length of up to 14 meters, with beams with a not very large section. After all, here miraculously, a beam with a single span turns into a continuous beam with two spans.
It is not necessary to calculate the mount of the strut, it is enough just to nail it from both sides, substituting under the rafter. This will not allow the strut to shift. The main thing - just cut the angle of the strut, given the slope of the foot rafters. To determine the cross-section of the beam required for rafter legs, it is necessary to calculate the compressive load.
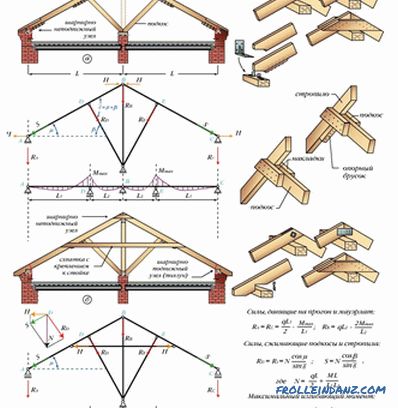
# 4. Rafters on subrafter beams.
If there are two supporting walls in the house, use two subrafter structures. They consist of beams laid along the long side of the roof. Below them are installed the racks on which the beams lie. Also supports for them are the floor and the inner walls of the house. If there are no runs, we put racks under each leg of rafters. The tops of truss legs are joined one to another and tied with steel or wooden linings. There is no ridge girder, therefore there is a thrust.
Tightening is set below the pass-through type of runs - so thrashing is canceled in the flow-free system. At the bottom of the racks for the stability of the fixing contractions. The bout, working as a bolt, takes compression loads. She does not give tilting racks. Stitches attach crosswise.
Example of installation of a truss system of a gable roof