Profile pipes are often used in the construction of metal structures, in creating greenhouse frames, making supports or masts subjected to vibration, when installing fences. Pipes are made of square and rectangular section, sometimes oval. Learn how to weld a profile pipe so that the product is durable and the seam is beautiful.
What is a profile pipe
 Profile pipes
Profile pipes
The profile pipe is a type metal, it is made by molding from a round pipe. After thermal deformation, metal stress is removed. The material for the product is carbon steel or stainless steel. The cross section of pipes ranges from 10 * 10 mm to 500 * 400 mm. The thickness of their walls is from 1 to 22 mm. Such pipes have significant advantages:
- A large selection of sizes allows you to choose the material for any metalwork.
- Standard sizes facilitate the joints of parts.
- Uniform pipe thickness allows for a reliable seam.
- The smooth surface of the product.
- The weight of the pipe is less than that of all-metal rolled products; the construction of it is made easier.
Before welding the profile pipe, it is worth considering the advice of professionals on the technology of the work. For welding steel pipes used known types of welding: electric, gas, contact and semi-automatic. Let us consider in detail how to cook a profile pipe in each of the listed ways.
Electric arc welding

The ease of use and high-quality seam, as well as the ability to use arc welding to work in hard to reach places, made this method very popular . Use for products with a wall thickness of more than 4 mm requires edge preparation. To work you will need a welding machine that can be rented if you do not have one.
The profile pipe is welded in various ways: with overlap, butt joint, T-joint or at any angle. Qualified welders advise the lower position of the seam, but you must be guided by your own conditions; you can use a horizontal or vertical seam.
For work, you will need:
- welding machine;
- electrodes;
- face shield and gloves;
- fixation device pipes;
- sandpaper and metal brush.
Electrode selection
 Electrodes
Electrodes
The quality of the connection depends on what electrodes to cook the profile tube. The electrode of small diameter will not provide the strength of the seam, and excessive thickness will lead to the burning of the pipe. A suitable electrode should maintain a steady arc and prevent oxidative processes.
Profile pipes of the same diameter are welded with non-consumable electrodes using argon as a protective gas.
The choice of the diameter of the electrode depends on the size of the pipe walls. For thin metal up to 2 mm, an electrode of Ø 1.5 mm will do; for a thicker metal of 2-3 mm, an electrode of Ø 2 mm is required. For metal of more impressive thickness - 4-6 mm, electrode Ø 4 mm is required.
 Assembly welding table
Assembly welding table
The parts for welding are fixed on a special table or made for this fixture. It is necessary to remove dirt and lubricants from them. A point-sticking of metal is performed to secure the structure. After alignment, the main process is performed. Welding arc lead with a speed that allows the edges to melt, but the metal does not have time to flow inside.
There is no general recommendation on how to perform welding correctly; the optimal speed is selected in a practical way.
For thin-walled pipes, welding is performed in one step, to join thick metal it will take several passes to weld all layers. Edging allows you to perform several seams and reduce metal stress. The mode of arc welding is affected by: current strength, polarity, electrode diameter, voltage, type of current. The current can vary from 20 to 90 amperes, it is calculated based on the thickness of the electrode. When working with thin metal, a direct current with reverse polarity is recommended.
During the welding process, slag is formed, which reduces the strength of the weld, and it must be periodically knocked down. After the seam has cooled, it is peeled off. Places heated to high temperatures rust faster, so they require thorough corrosion protection.
Gas welding
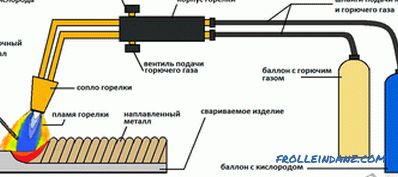
The work requires:
- oxygen cylinder;
- reducer;
- cylinder with acetylene;
- filler rods;
- burner and tips;
- hoses to supply gas to the burner.
 Welding of metal
Welding of metal
The welded construction requires fixing and cleaning the surface, with the thickness of the metal wall from 5 mm the bevel of an edge is carried out. Pre-coating the surfaces to be welded with flux will create a film that protects against oxidation and makes the seam stronger. Combustion maintains a mixture of oxygen and acetylene, with the result that the molten metal fills the gap. This method is less common due to the fact that it is more expensive, and work with gas equipment is more dangerous, and requires professional training of a gas welder.
To improve its quality allows the additive, which is selected specifically for this purpose. For pipes with thin walls, a right-to-left welding method is used. The filler bar is fed in front of the burner. The uniform melting of the additive and the edges makes it possible to form a reliable and neat seam. The coating of the weld with flux creates a film that protects against oxidation. Thick-walled tubes are stitched from left to right, the additive is located behind the burner. After cooling, the seam will require improvement. Each stage requires verification of the geometry, in identifying distortions it is necessary to level the structure.
Gas burners should not be used to connect thin-walled butt-shaped tubes due to the high temperature, since the edges of the products melt and deform.
Gas welding is a more costly method, since buying acetylene is significantly more expensive than electricity used for arc welding. But in the absence of a power source, it becomes indispensable.
Resistance welding

This method is not widely used in everyday life and is used only by professional welders. It is used in places where special equipment is installed. This complex type of welding is carried out due to the pressure of the electrodes on the parts and with the simultaneous transmission of electric current. The process takes place without the use of additives. Resistance welding ensures reliable edge bonding. Plastic deformation from compression and a short-term increase in temperature due to current transmission form an integral metal connection.
Useful tips
 Sturdy frame made of shaped pipe
Sturdy frame made of shaped pipe
Welding shaped pipes with your own hands has several secrets:
- The deformation due to high temperature is more pronounced than that of round pipes.
- Melting of the metal can lead to overlapping of the internal space. In the case when the hollowness of the pipes is important, you need to make sure that there are no drops of metal inside the product.
- The end connection provokes the appearance of high voltage at the corners due to uneven heating and improper formation of metal rollers.
Having a little experience with a welding machine, you can easily weld the necessary construction of shaped tubes. Videos with explanations from professional welders will help to understand the details.
Video
This video shows how semi-automatic welding of profile tubes is performed using welding wire:
This video is not of an educational nature. The method shown allows, without skill, to weld a rather thin butt-joint profile without burning it: