As a rule, the question of how to sheathe a wooden house outside arises at the design stage. It is solved on the basis of the analysis of climatic conditions in the area of construction and design considerations. It is the combination of protective properties and aesthetics that should be the basis of the choice of exterior finishes. Then, out of several options, usually there are 2–3 of them, the one that is most appropriate in terms of financial parameters and technical capabilities is selected.

Purpose of the cladding for a wooden house and the rules for the selection of material
The wooden house is one of the most eco-friendly, comfortable and technologically advanced in construction. But wood is a relatively short-lived material, if it is not protected from external influences. It rather actively absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and when directly exposed to rain or snow, is prone to its accumulation. As a result of exposure to water, ultraviolet and oxygen, the tree darkens, loses its density, begins to rot and decay.
With an excessive amount of moisture, spores of mold, fungus, and moss settle in the tree, which have a negative effect. Also, the tree is exposed to insects, rodents and other pests.
Wood protection consists of treating a material with various chemicals - impregnations, paints, paints, varnishes and covering facade walls with other materials - clapboard, siding, and plaster. The second option does not exclude the use of chemical protection (in many cases it even provides for it) and is aimed more at enhancing the thermal and moisture characteristics of a wooden house and at improving the aesthetics of a building.
The main tasks of the cladding are:
- protecting the walls from external influences;
- creating a barrier to heat loss;
- home decoration.
When choosing a plating option, there are certain rules regarding the physical properties of the plating, its cost, and the manufacturability of the installation and maintenance.
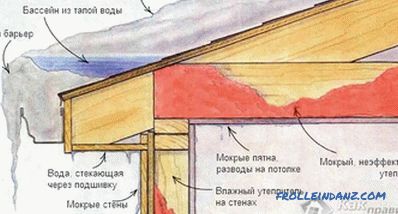
To begin with, it is necessary to consider a property such as vapor permeability. Wooden walls "breathe" - they are able to accumulate moisture from the atmosphere or the interior of the house and give it away when the external conditions change. It is impossible to make the outer casing completely airtight - it must ensure free gas exchange with the external environment, that is, be vapor permeable. In this case, the vapor permeability of the skin should be greater than the wall mass. This will remove excess moisture outside, not inside the house.
If this rule is not observed, moisture will accumulate at the contact boundary of the two materials and form a zone of high humidity - an exceptionally favorable environment for the development of rot, mildew and other phenomena unpleasant for the tree. At low temperatures, the water, if it has accumulated enough, will freeze and turn into ice, which, expanding, can destroy the lining.
If the house is sheathed with vapor-proof material, a ventilated facade should be installed. The essence of the design is that the outer vapor-tight or relatively vapor-permeable layer is 60–150 mm from the wall surface. In the lower and upper parts of the skin, holes are left through which natural air circulation takes place and excess moisture is removed by convection currents.
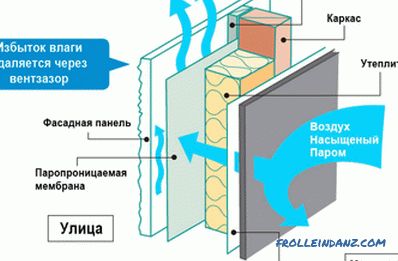
Ventilated facade device.
Some difficulties with the installation of external cladding may give rise to the idea - is it really necessary? With good reason, you can answer positively. Not just needed, but necessary. Even if you like the look of a log house or a flat bar, sooner or later you will have to sheathe the house.
A tree must be treated with protective agents at regular intervals. This entails significant costs that increase the cost of operation. If you choose the right material and make the finish, then operating costs on an annualized basis will be much lower.
Natural wood materials used for exterior plating of a wooden house
When choosing the better to sheathe a wooden house from the outside, materials from natural wood will inevitably come into view:
- lining;
- block house;
- imitation lumber;
- planken.
All of them have obvious advantages, like natural material, but also have the same disadvantages as any wooden product. This leads to the fact that, in addition to the cost of purchasing the material, it is necessary to incur certain expenses for finishing with antiseptics and coating varnishes and paints.
Wall paneling
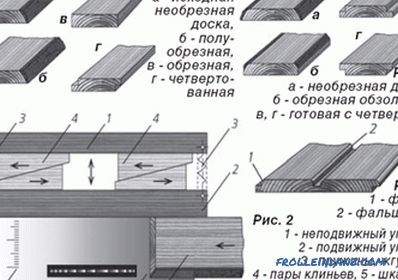
The cheapest and most technologically advanced type of natural wood siding is slats with shaped sides forming a groove / tongue connection. At installation, the wall paneling firmly and tightly connects and forms an almost monolithic surface.
For decoration, dry lining is used exclusively, humidity not higher than 10 - 15%.If you use insufficiently dried wall paneling, it will inevitably dry out and gaps will appear along the mating lines.
There are several standards for lining, the average dimensions of it are:
- thickness - 12 - 40 mm;
- width - 76 - 200 mm ;
- spike length - 4 - 5 mm;
- length - 2 - 6 m.
Mounting of the panel is made in a horizontal position, starting from the bottom, with a spike up. If you set it up with a groove, the water flowing down the wall will fall into the lock and over time will destroy it and the wall paneling itself. With proper installation and proper care, the lining of the wall panel will last 10 to 15 years, and if it is soaked with modern antiseptics, it will last longer.
The advantage of such a plating is low cost and ease of installation. Anyone who can hold a hammer and use the building level can handle the installation.

Imitation of a bar
It is the same prefabricated surface as the wall paneling, but differs somewhat in appearance. It is also installed horizontally, only visible joints are practically invisible. After the final installation has the form of a wall, folded from the profiled bar. It is made from spruce, pine, cedar or larch, due to the resinousness of these species is quite durable.
Material is produced in the form of planks 2–4 m long, 20–35 mm thick, and 105–175 mm wide. You can buy a solid board, cut from one log, or spliced, glued under pressure from narrower slats. In terms of performance, both types are about the same.

Pros and cons are similar to wall paneling. The imitation of the timber wins only in appearance - the material is more modern and decorative.

Block House
Excellent finishing material, made in the form of boards with a semicircular outer side. When assembled, the material creates the appearance of a log cabin. Very decorative, durable and in installation no more difficult lining. Compared with clapboard and imitation of timber, the block house is more durable, it keeps heat better and is much more durable.
For the manufacture of lamellae, conifers of wood are used, in most cases pine and spruce. Impregnation with various stains, azure and scanting materials allows you to give the finish look of any valuable wood species. When painting with oil or alkyd paints, most of the effect of the use of a block house disappears (in the case of imitation of a bar this does not happen).

The block house is also notable for its good thermal performance. Compared to previous materials, it keeps heat better in the house and lets the cold inside worse. But the cost of plating this material is higher.

Planken
Comparatively new material in our latitudes. It is a facade board with beveled or rounded side edges. It is made of pine, larch or wood-polymer materials. The width of the board is in the range of 70 - 140 mm with a thickness of 15 - 20 mm, the bevel angle of the faces - 45 - 70 0 . Mounted on special mounts in spike or overlap.


Very useful for mounting ventilated facades. As a rule, it is sold in a form treated with fire retardants and antiseptics, therefore it is resistant to biological pests and is safe in the fire sense.

In most cases, high-quality planken is impregnated with environmentally friendly means, but it will not be superfluous to check the certificate upon purchase. Cheap materials can be treated with toxic reagents.

Siding for exterior cladding of a wooden house
A material specially created for facades. It is made in the form of special-profile lamellae ("herringbone" or "ship"), with locks on the long side and a special perforation for nail fastenings. The lamellas interconnect with special snaps and form a dense coating.
Siding is made of various materials:
- polymers;
- metal;
- cement-bonded particle materials.
The width of the slats varies from 10 to 30 cm, and the length is 2 - 6 m. Like wooden facing materials, the siding is installed in a horizontal position with such an arrangement of the profile that rainwater will certainly flow down without getting inside the wall.
The variety of color solutions and ease of installation determined the exceptional popularity of siding in facing various types of buildings - from residential buildings to industrial, commercial and public. In addition to the lamellas themselves, a wide range of core parts is made - internal and external corners, cornices, connecting strips, etc.
The external texture of the siding, regardless of the material, usually imitates the natural wood pattern. Lamellas are coated with a polymer coating or weather-resistant paint that also has high strength - it is quite difficult to accidentally scratch siding.All materials used for the manufacture of siding, have a high weather resistance and almost not subject to moisture. The service life of siding is several decades.
Compared to wood paneling, siding has the advantage of not requiring maintenance. From time to time it is enough to simply wash it with clean water or any of household detergents without abrasive additives. When considering how to sheathe a wooden house outside, it is necessary to pay attention to this feature. Varnishes and paints are not required. Having paid for the material and installation once, you can be calm for 15 - 20 years for the appearance and condition of the facades.
Vinyl siding
Vinyl siding is lightweight and does not require heavyweight support frames. It can be installed on any frame or panel house - it is enough to fix the rack frame on the walls.

Since this material is not capable of passing steam, its installation should be done only on the ventilated facade.

Metal siding
Galvanized steel siding has gained ground only in the past few years. Profiled strips with locking joints 120–550 mm wide are covered with a layer of powder paint and polymer protection and roofing sheeting are not inferior in strength and durability.

The life of such a coating exceeds 50 years. Metal trim is installed only on ventilated facades.

Cement siding
Also recently, cement siding has become widespread. It is a fiberboard mixed with cement mortar and pressed into profile panels. Production takes place at a high temperature at which cement is sintered and acquires some properties of ceramics.

Such a siding is extremely durable, but it has a lot of weight and requires a strong frame. The panels are made in the form of primed products with different surface texture. They are designed for painting with special paints.

Other ways of finishing the facade of a wooden house
There are some materials that are not so often used for wall cladding of a wooden house, but consider them as a facing material all worth it. First of all it concerns such materials as a professional flooring and facing bricks.
Facing brick
The brick facade of a wooden house is now a rarity. But he has the right to life, thanks to the exceptionally high strength, frost resistance, decoration. But when installing a brick facade, it is necessary that the house be on a concrete foundation - the weight of the wall, even half the thickness of a brick, is quite impressive.
Installation of a brick facade is carried out only after complete shrinkage of the wooden house, otherwise damage is inevitable. A ventilation gap of at least 5 cm between the finish and the wall is absolutely necessary. The attractiveness of the brick facade is also in the fact that it does not require any care. The natural look persists for many decades.

Professional sheet
In addition to special facade materials, the walls of a wooden house can be sheathed with ordinary professional sheets. The professional sheet is made of galvanized steel coated with a polymeric protective coating. Usually this material is used for finishing technical constructions. But thanks to a wide range of design solutions, today professional flooring imitating wood, stone or brick is being produced. Therefore, it can be used with complete success to decorate walls or individual fragments of the facade of residential buildings. The advantages of this material can be written down: absolute resistance to negative environmental factors, not exactingness in additional protection and maintenance, non-flammability.
The main disadvantage of the material is its inability to pass steam. That is why it can only be used for cladding ventilated facades. In addition, when exposed to the material of strong mechanical loads, it can be bent. At the same time, it is practically impossible to bring the material to its original smooth state.