Among the materials used in the construction and production of furniture, chipboard takes an important place. What is chipboard, what types of material exist, what are the applications and level of manufacturability of the material, how to use it and what to expect from it? Answers to these questions will give an overview of the properties and characteristics of chipboard.

What is chipboard
Chipboard is a sheet material obtained by pressing from small wood shavings that are bonded to each other with glue. The idea of creating such a composite appeared in 1918. Initially, it was proposed to make a slab of chips with double-sided veneer. In the following decades, the manufacturing technology was refined and improved. The first commercial plant for the production of particleboard earned in 1941 in the German Bremen. The wide distribution of wood waste plates began after the end of the war.
Interest in the new material is due to several reasons:
- the simplicity of obtaining large-sized parts;
- the stability of shape and size;
- using waste as a raw material instead of scarce wood.
Due to the mass production of chipboard, the number of irretrievable losses of wood during harvesting and processing of wood has been reduced from 60 to 10%, and the construction and furniture industry have received convenient, technological and cheap material.
Types of chipboard
There are several types of chipboard:
- pressed;
- laminated;
- moisture resistant;
- extrusion.
1. Pressed chipboard has sufficient strength and is used as a structural material in construction and for furniture production.

2. Laminated chipboard is a pressed plate, lined with a layered coating of paper, impregnated with melamine-formaldehyde resins. Lamination increases the surface hardness and wear resistance of the plate. On paper printed pattern, which serves as a decor. In the process of coating, it can be given a texture that enhances the decorative qualities of the laminate.

3. Moisture-resistant chipboard, is intended for use in wet conditions. Its resistance to moisture is achieved by the addition of hydrophobic additives to the composition of the binder.
4. The extrusion (extruded) plate does not have the strength of the extruded one, since it compacts less and the chips in it are perpendicular to the plane of the plate. This material is used for sound insulation.
Pressed laminated and non-laminated chipboard - the most common and popular types. It is about them will be discussed further.
The pressed plates, in turn, are subdivided according to several parameters: By strength
According to the structure - to ordinary (О) and small-structure (М). For lamination, slabs of group M are preferred, since they are best placed on cladding.
On surface treatment - on ground (Ш) and unpolished (НШ).
According to the quality of the surface - on grades I and II, for each of which a list of acceptable defects and their number is determined in GOST.
According to emission class - to classes Е0.5, Е1 and Е2. They differ in the maximum permissible content of formaldehyde in the material and its release into the air. For indoor use, only classes E0.5 and E1 are permitted.
How chipboard is made
Non-commercial wood and almost any wood waste generated by any kind of treatment, starting with tree felling, is suitable for making wood-based particle boards: round timber and branches;
Production consists of several stages.
Preparation of raw materials
Lump wastes are ground into chips. Chips and large chips are used to produce chips of required dimensions: from 0.2 to 0.5 mm thick, 5–40 mm long, and up to 10 mm wide.
Kruglyak is cleared of bark, cut into measured segments, as a rule, 1 m long, and after soaking it splits along the fibers into small fragments, followed by grinding to the desired condition.
The slab has a three-layer structure. The outer layers are made from small chips, and the core - from larger ones. Therefore, the chip mass is divided and the part that is intended for the outer layers is additionally crushed. After drying, sorting takes place. With the aid of sifting, the unsuitable fractions are separated and redistributed, and too large chips are returned for grinding.

Forming and pressing
The prepared chips are mixed with a synthetic resin, which is part of the chipboard as a binder.This operation is performed in a special machine, where the resin is sprayed into small drops and settles on the surface of wood particles "suspended" in the air stream. This mechanism allows you to glue the entire surface of the chips and prevent excess resin.
The tarred chip enters the dosing unit, which lays it on a conveyor belt or tray, forming a layer of a given thickness. Three layers are consistently placed in accordance with the three-layer structure of a particle board. The resulting "carpet" is divided along the length of the standard package size, and served in the vibropress for pre-compaction. After pre-pressing, briquettes are obtained that can withstand movement to the main hydraulic press.
Before pressing, briquettes are heated to 75 o C with microwave radiation. In the press, they are exposed to temperatures of 150-180 o C and temperatures of 20-35 kgf / cm 2 . Under the action of pressure, the material is compacted, and heating causes hardening of the binder.

Full availability
After pressing is completed, the ready-made sheets of chipboard are cooled with air flows, then placed in the feet and left for several days. During this time, the temperature in the material is gradually equalized and internal stresses are removed.
Before full readiness, the material is ground and cut into sheets of a given format. After that they are marked and packaged for shipment to the consumer. In the manufacture of furniture or cladding plates, a lamination step is added to the process chain.

Standard sizes of chipboard sheets
Production offers several standard sizes of chipboard sheets:
- 2440х1220 mm;
- 2440x1830 mm;
- 2750x1830 mm;
- 2800x2070 mm.
The latest format in this list is not provided for by Russian GOST, but some foreign companies supply laminated sheets of this size. The thickness of the material usually corresponds to the standards adopted in furniture production: 10, 16, 18, 22 and 25 mm.
Maximum permissible deviations of dimensions in accordance with GOST 10632-2014:
| By thickness, mm | by length, mm | By width, mm |
|---|---|---|
| +/- 0.3 - for ground | +/- 0.5 | +/- 0.5 |
| -0.3 / + 1.7 - for unpolished |
Main characteristics of chipboard
Strength and density of particleboard
Strength of particleboard is determined by its belonging to one of two groups - P1 or P2. P2 plates have a higher bending strength - 11 MPa against 10 MPa in group P1. They are almost one and a half times more resistant to delamination. The density of sheets of both groups is 550 - 820 kg / m 3 .
One aspect of strength is the ability to hold fasteners. The screw, twisted into the plate surface, can withstand the pulling load from 3.5 to 5.5 kg per millimeter of length. When installed in the butt, the ultimate force is less - 3.0-4.5 kg / mm.
| Indicator | Plate P1 | Plate P2 |
|---|---|---|
| Density, kg / m 3 | 550-820 | |
| Impact strength, J / m 2 | 4000-8000 | |
| Hardness, MPa | 20-40 | |
| Resistivity of pulling screws, N / mm, from the surface | 55-35 | |
| Resistivity of pulling the screws, N / mm, from the edge | 45-30 |
Moisture resistance of chipboard
Chipboard resistance to moisture is not regulated. This material is intended for dry conditions only. Although there are its moisture-resistant versions, which are produced with the addition of a water-repellent agent.
Biological resistance
The biological resistance of chipboard is quite high. They are not damaged by insects, they do not take root fungus. The stove can be completely destroyed by moisture, but it will not rot on it.
Fire safety
When assessing the fire hazard, chipboard should be counted as wood. The composite belongs to the same group of flammability G4, although it lights up and spreads the fire is not as willing as wood.
Environmental friendliness
DSP is quite safe for people, but when using it, attention must be paid to the emission class, which depends on the level of formaldehyde emission into the air. Material of class E2 cannot be used inside premises, for this purpose E1 class plates are intended. For children's rooms, schools, kindergartens, nurseries, hospitals should use plates of class E0.5, which contain a very small amount of formaldehyde and their effect on the composition of the air in the room is negligible.

Thermal Conductivity
The insulating qualities of particle board are small, but they should be taken into account when using it as a wall covering, ceiling or floor. The average thermal conductivity of the plates is 0.15 W / (m ∙ K).At a thickness of 16 mm, the thermal resistance of the skin per square meter will be 0.1 (m 2 K) / W. For comparison: a ceramic brick wall 390 mm thick has a thermal resistance of 2.22 (m 2 ∙ К) / W, and a layer of mineral wool 100 mm thick - 0.78 (m 2 ∙ K) / W. And yet, sheathing of chipboard, especially with the air gap behind it can be a noticeable addition to the insulation.
Vapor permeability
Water vapor permeability is an important characteristic of chipboard, if it is used in external enclosing structures. With a permeability of 0.13 mg / (m ∙ h ∙ Pa), the material cannot serve as a vapor barrier, but when it is lined outside, good vapor permeability will help remove moisture from the wall.
Manufacturability of chipboard
In terms of convenience and economy of use, chipboard is much more than wood. This parameter has no numerical expression, but several facts can be given to illustrate the advantage of the particle board in this respect.
Minimum operations in the manufacture of products
In order to make furniture or other construction from chipboard, you need to perform several basic actions:
- sheet cutting into details of the desired dimensions;
- drilling out of holes and sockets for fasteners and fittings;
- fitting and assembly.
In many cases, drilling out as a separate operation is absent. When using a laminated plate, painting with concomitant preparation is not required, only a lining of edges is needed, which is made on special machines and does not require much effort.
The most difficult operation in the manufacture of furniture is the cutting out of parts of complex curvilinear shape. But the number of such parts, as a rule, is small.

Compare the listed with the actions required for wood products:
- sawing;
- planing ;
- final planing (gauge);
- cutting into parts;
- milling, often necessary for joining parts;
- sealing of defects;
- polishing;
- painting.
If larger parts are required, then operations of gluing a shield from the rails or assembling a large piece of small parts are added, since the width of wooden boards usually does not exceed 300 mm. Countertops and cabinet doors are made in this way. And this is only the preparation of parts that need to be connected to the product!
Easy assembly operations
When fitting accessories to parts made of chipboard, drilling for fasteners is often not required. For wood, it is needed more often, especially for hardwoods. Drilling chipboard is easier than wood. The chipboard is less demanding on the accuracy of mounting hardware and accessories. All this reduces labor costs in production.
Stability of products
Chipboard, unlike wood, does not change dimensions when humidity fluctuates. Details from it will not crack in the summer heat, they will not be jarred, there will not be an extra gap or strip of undyed surface anywhere, as is the case with wooden doors. During normal operation, a chipboard product remains unchanged for many years.
Fields of application chipboard
Chipboard is used wherever large parts are required.
Furniture production
A laminated plate is used in furniture production. This immediately removes the surface cladding issues. The choice of decors is very large and allows you to satisfy almost any requests. Despite some plasticity of the material, the correct location of the parts gives the products excellent rigidity.
Most often, the chipboard is made of:
Kitchen furniture.
A furniture range is almost always a set of modules made of chipboard.

Writing and computer desks.
It is convenient to make all kinds of tables, shelves, superstructures, partitions from flat parts.

Cabinets, including built-in wardrobes, shelving, filling wardrobe rooms.
In this furniture large parts predominate, and board material is best suited for this.

In some cases, the weight of the furniture is important. It can be calculated in advance, knowing how much a chipboard sheet, its area, and the total area of parts of the product weigh. For example, for the manufacture of a desk or a small wardrobe you need one standard sheet of 2750x1830 format. With a thickness of 16 mm, it weighs 57 kg. About as much and will weigh a table or cabinet. For a more accurate calculation, use the specific weight of the plate - 11.4 kg per square meter. Bringing in the table the dimensions of all parts, it is easy to calculate the weight of the product.
Construction
Examples of the use of chipboard in construction:
- sheathing of frame structures;
- interior finish;
- creation of volumetric elements of the interior;
- manufacturing of partitions;
- leveling the floor under the finishing floor;
- manufacturing of formwork and auxiliary structures.
In construction, the most commonly used non-laminated chipboard.

For any use, you must eliminate the possibility of moistening the material.
- Exterior cladding of frame walls is permissible only under a hinged ventilated facade.
- Constructions reaching the floor, such as partitions, must be protected from moisture. For this, a gap of 10 mm along the bottom edge is sufficient. The gap is blocked by a plinth.
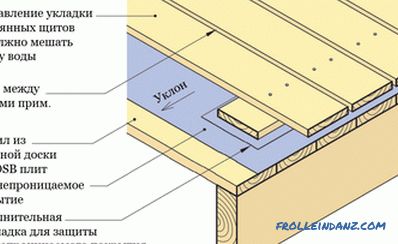
- When used as a subfloor, high-quality waterproofing must be done.
- For making the formwork, the working surfaces must be protected with a film.
For any application, it is important to choose the right stove with suitable characteristics. And then the desired result will be obtained.