Wood rot is the price nature assigns for the organic origin of this remarkable ecological building material.

Wood rot occurs due to a favorable environment for the development of microorganisms.
Parasitic fungi find an excellent nutrient medium in wood and, due to their vital activity, provoke decomposition of sawn timber and destruction of wooden structures. However, the loss of the biological properties and technical qualities of the tree occurs only if there are favorable conditions for the development of colonies of the simplest organisms.
Causes of putrefactive processes, their types and stages
Biological destruction of wood is triggered in the following circumstances:

Wood decay often is due to dampness.
- a damp and warm climate;
- having oxygen access;
- the internal humidity of the wood itself is above 18-20%.
These factors provide an opportunity for various fungi to parasitize on wood and cause putrefactive processes. Thus, freshly cut logs in the areas of logging and piles of lumber in warehouses can affect warehouse and pillar mushrooms. A building materials and wooden structures made of wood, both hardwood and coniferous, may suffer as a result of the wood-destroying effects of many varieties of house mushrooms (real, white, membranous, etc.).
The type of rotting depends on the physical properties of the tree and the type of fungus that parasitizes on it.
With a destructive type, triggered by a larch sponge, sulfur-yellow, bordered and other tinder:

When rotting, wood cracks appear .
- Wood becomes smaller in volume.
- Cracks manifest.
- The color of the tree varies from a reddish color to brown and dark brown.
- The wood structure becomes brittle.
- There is a disintegration of wood into pieces in the form of cubes and prisms, then it crumbles into powder.
With a corrosive putrefactive lesion:
- Wood does not lose viscosity and volume.
- Destructions are partial and alternate with healthy zones.
- In the wood material, cells and pits first appear, then it begins to stratify into fibrous layers.
- The color of the wood affected by the fungus becomes variegated (white foci on a brown base) or very light (white, light yellow or marble).
The cause of the motley rot is mushrooms such as sponges (pine, root, spruce) and tinder (oak, spruce butt). The white color is caused by honeydew and tinder (flat, false, real).
Stages of the destruction process
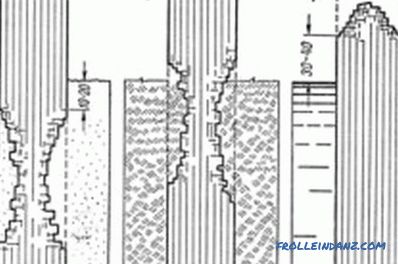
Destruction of wooden poles in different conditions: a - in sandy soil, b - in dense clayey soil; in - a pile in a reservoir.
In order to assess whether it is possible to use affected wood for technical purposes, it should be determined at which stage of decay it is. The process of decay of the tree goes through 4 stages:
- Initial. Mushroom mycelium does not affect the tree's sheath Wood still retains its structure, strength, only changes color to olive, lilovo-gray or red-brown.
- Developed. Cracks or pits appear in the wood. Light streaks and mycelium films appear on a brown background.
- Ultimate. The tree completely loses its strength, crumbles or splits into chips. Color is fully consistent with the type of rotting.
- Mechanical destruction of wood, the formation of a hollow.
When working with wood, you should always take into account the tendency of this building material to be affected by fungus and, depending on the desired result, prevent decay or accelerate rotting.
How to deal with wood rot?
Prevent the development of fungi and the penetration of mushroom spores into the core of the tree should be already in the process of production and storage of material. After all, after felling its humidity is close to 40%. To prevent putrefactive processes, such protective measures as natural and industrial drying of sawn timber are applied.
When natural drying, harvested lumber must be laid for at least 1 year. During industrial drying, this process is significantly accelerated due to the method of heating lumber to 80-100 degrees. This is the sterilization of building materials with the disposal of his mycelium and spores.
To prevent the wood from rotting, it must be treated with special compounds.
The treatment of wood with various water-soluble and oily antiseptics helps to stop rotting. In domestic conditions, surface antiseptic wood protection is performed. Walking a few times with a brush or spray to apply an antiseptic, you can safely soak the top layer of wood.
For deep impregnation, industrial power is needed, since it is carried out by immersing wood elements for several hours in hot-cold antiseptic baths or using an autoclave. However, even very high-quality dry material during its operation may be subjected to putrefactive infection.
Protection against the development of putrefactive processes in wooden structures Measures of protection from infection of wood with mushrooms and mold are as follows: 
Proper waterproofing of the basement will protect the house from rotting.
- Construction of basement waterproofing, drainage system for removal of groundwater and surface water.
- Wood coating with paints and varnishes.
- Existence of a moisture-proof roof of the building.
- Creating room ventilation with air vents.
- Proper installation of insulating layers on the walls of structures to prevent accumulation of condensate (vapor barrier is inside the room, and the insulating membrane is outside).
- Protection of the ends of the logs by particularly careful treatment with antiseptics or their additional boarding.

Proper waterproofing of the basement will protect the house from rotting.
In the case when the wooden structure is subjected to periodic moistening, only potent antiseptic agents stop rotting (for example, Neomid 400, Neomid 500, double-acting chemicals that protect against moisture and rot). In this case, the already decayed wood is completely cut down, removed from the room and burned in order to avoid further infection of the tree.
For the purposes of prophylaxis, wooden buildings should be carefully inspected annually for damage by parasitic fungi. Upon detection of lesions, either a complete replacement of the wooden element or cutting down of the infection zone and subsequent antiseptic treatment is performed.
How to accelerate the process of wood decay
Sometimes the susceptibility of wood to rot can be regarded as a positive point. If you know how to speed up decay, you can use this feature of natural material to your advantage and force the fall of a tree or the removal of a stump.
Tips on how to speed up decay to remove dead trees and stumps are as follows:
- Drill more holes in them a couple of centimeters deep. Insects will collect in these gaps, and during precipitation - moisture will accumulate. Thus, the rotting of cellulose will accelerate, and the wood will decay much faster.
- It is possible to accelerate rotting, if spores or pieces of mushrooms taken from already decayed wood of the same species are poured onto a tree or stump.
- Pour nitrogen fertilizer around the waste trunk, which will trigger the development of fungus parasites. After some time, you can feed the fungi with sweet water to stimulate the growth of their population.
All these tips can be used simultaneously. And, of course, should often water the trees, moisten stumps. Then favorable results will not keep you waiting too long.
Didn't find the answer in the article? More information on the topic:
-

The process of painting a wooden floor
Recommendations for how to self-paint a wooden floor. Selection of necessary materials, tools. The process of painting and method of work.




